E-invoicing (electronic invoicing) is the automated exchange of invoices in a structured digital format, such as XML or EDI (electronic data interchange), between businesses and tax authorities. Unlike PDF invoices, e-invoices integrate directly with ERP systems, improving accuracy, compliance, and efficiency. In this guide, we explore what e-invoicing is, how it works, its benefits, global regulations, and how businesses can implement it effectively.
Key takeaways
- It automates invoice creation, validation, and processing, improving accuracy and efficiency.
- Governments worldwide are mandating e-invoicing to enhance tax compliance and reduce fraud.
- Businesses benefit from faster processing times, cost savings, and reduced manual work.
Understanding E-Invoicing
As businesses move toward digital transformation, e-invoicing innovates financial transactions, improving efficiency, security, and compliance. E-invoicing, or electronic invoicing, generates, sends, receives, and stores invoices digitally. (Source: Thomson Reuters)
In the United States, adoption is gaining momentum, with a reported rate of 25% by U.S. companies. This digital shift is driven by the potential for significant cost savings, with automated electronic invoicing resulting in cost reductions of 60-80% in most cases. (Source: Pagero)
What is E-Invoicing?
E-invoicing (electronic invoicing) is the digital exchange of invoice documents between businesses, suppliers, and customers in a structured format. Unlike traditional paper or PDF invoices, they are processed electronically in XML, EDI, or UBL formats. (Source: Basware)
As the global e-invoicing market reached $13.5 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 17.7% from 2024 to 2032, reaching $60.9 billion by 2032, more businesses are recognizing the multifaceted benefits that e-invoicing brings to the table. (Source: High Radius)
Key characteristics of e-invoicing
E-invoicing involves more than sending invoices electronically—it involves automating and structuring financial data to ensure seamless processing, compliance, and integration with business systems.
- Machine-readable structured data (e.g., XML, EDI, UBL): Unlike PDFs or scanned invoices, these use structured data formats, which make them easily readable by accounting software and tax authorities. This eliminates manual data entry, reduces errors, and enables automated validation.
- Secure Electronic Transmission – They are sent through encrypted, standardized communication protocols, reducing the risk of fraud, interception, or unauthorized modifications. This ensures data integrity and compliance with tax regulations.
- Seamless Integration with Accounting and ERP Systems – E-invoices can be directly imported into enterprise resource planning (ERP) and accounting systems, enabling faster processing, automated approvals, and real-time financial tracking. This improves efficiency and reduces the administrative burden on finance teams.
- Not Just a Scanned PDF; It Must Be a Structured Digital Format – A scanned invoice or PDF does not qualify as an e-invoice because it still requires manual processing. A true e-invoice is structured, machine-readable, and compatible with automation tools, ensuring faster processing, compliance with regulatory standards, and enhanced data accuracy.
What doesn’t qualify as an E-Invoice?
Not all digital invoices meet the criteria for electronic invoicing. Many assume that sending a PDF or an email with invoice details qualifies. Still, unless an invoice follows a structured format and integrates seamlessly with accounting systems, it does not count as an e-invoice.
- Scanned paper invoices: Even if converted into a digital format (e.g., PDF or JPEG), scanned paper invoices lack structured data for automated processing.
- PDF or Word invoices: Invoices generated in PDF or Word formats and emailed as attachments are not e-invoices since they require manual handling.
- Email correspondence with invoice details: Text-based invoices sent via email without structured data integration.
- Unstructured digital formats: Any invoice file that does not follow a machine-readable standard (e.g., Excel invoices without a structured schema).
- Paper-based invoices with QR codes: Even if they include a digital component, they still require manual entry unless they are integrated with e-invoicing platforms.
How E-Invoicing differs from Traditional Invoicing
Traditional invoicing methods rely on manual data entry, paper invoices, PDFs, and email-based transactions, often leading to delays, errors, and inefficiencies in financial workflows. In contrast, e-invoicing automates invoice generation, validation, and processing, enabling faster, more secure, and compliant transactions.
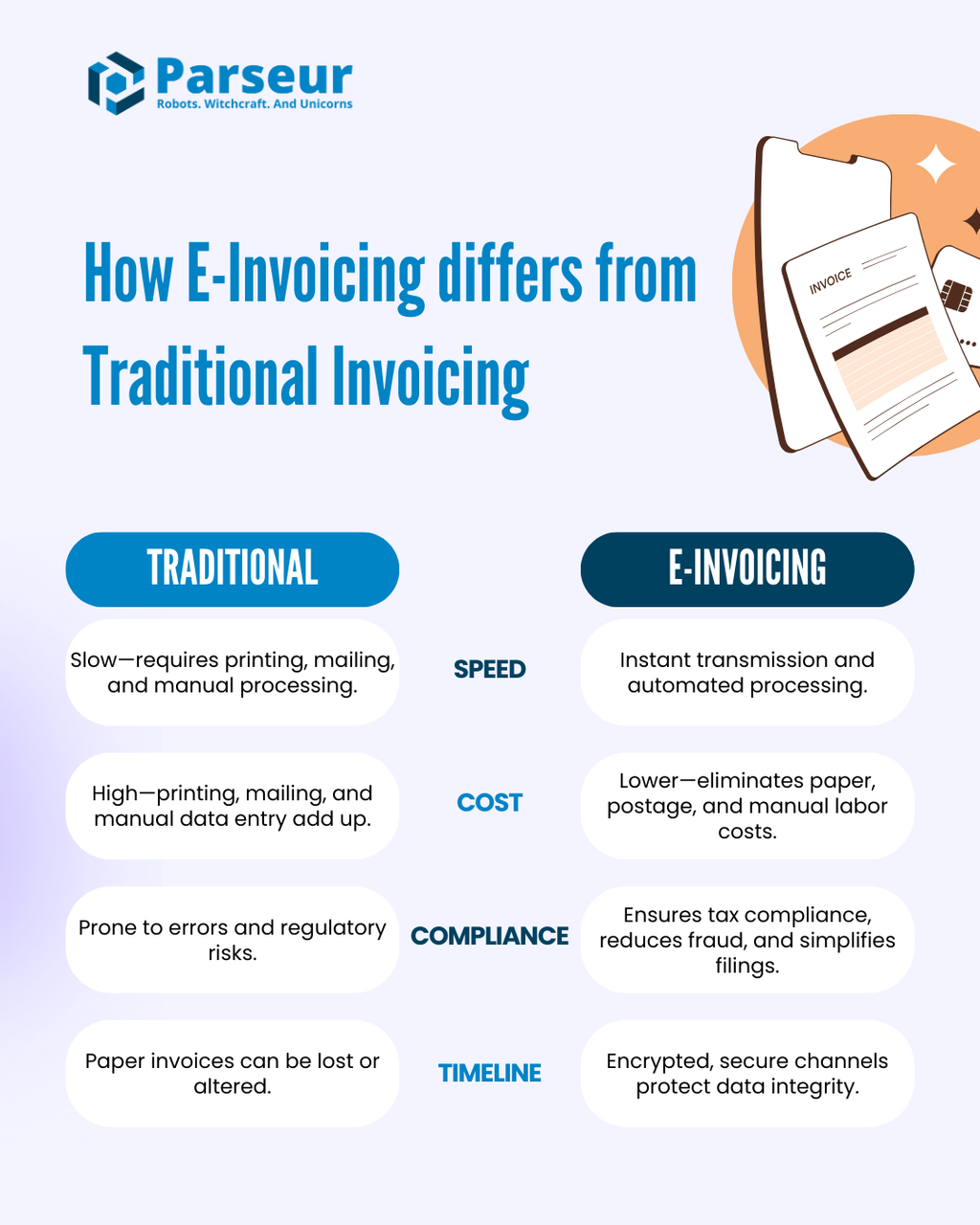
Here’s how e-invoicing outperforms traditional invoicing:
- Speed & Efficiency – Traditional invoices require printing, mailing, and manual approval, which can take days or weeks. E-invoicing automates real-time invoice transmission and processing, reducing payment cycles and improving cash flow.
- Cost Savings – Paper-based invoices incur printing, postage, storage, and manual processing expenses. E-invoicing eliminates these costs, significantly saving administrative and operational expenses.
- Error Reduction & Accuracy – Manual invoicing is prone to human errors, duplicate entries, and lost documents. E-invoicing ensures automated data validation, reducing discrepancies and improving invoice accuracy.
- Regulatory Compliance – Traditional invoicing often lacks built-in tax validation, increasing the risk of compliance issues. E-invoicing automatically aligns with tax regulations, simplifying VAT reporting and reducing fraud risks.
- Security & Data Integrity – Physical and email-based invoices are vulnerable to forgery, loss, and unauthorized alterations. E-invoicing uses encrypted channels and digital signatures, ensuring that invoices remain tamper-proof and verifiable.
Types of E-Invoicing systems
E-invoicing systems vary based on how invoices are transmitted, processed, and integrated within business and government frameworks. The right system depends on regulatory compliance, business size, and transaction volume. Below are the most common types of e-invoicing systems:
1. Peppol E-Invoicing Systems
Best for: Businesses operating in Europe, Australia, Singapore, and U.S. federal procurement that require standardized, cross-border e-invoicing.
Peppol (Pan-European Public Procurement OnLine) is a global e-invoicing framework that enables businesses and governments to exchange invoices securely using a standardized format and certified Access Points. Peppol ensures VAT compliance, tax reporting, and fraud prevention.
Examples of Peppol Providers are Basware, Pagero, and Tungsten Network.
2. Direct EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) E-Invoicing Systems
Best for: Large enterprises and supply chain businesses needing automated, high-volume invoice transactions.
EDI is a machine-to-machine data exchange system allowing businesses to electronically transmit invoices and other documents using predefined formats (EDIFACT, ANSI X12, XML, UBL). It is widely used in manufacturing, retail, logistics, and healthcare industries.
Examples of EDI Providers: IBM Sterling, OpenText, SPS Commerce.
3. Government-Mandated E-Invoicing Systems
Best for: Businesses required to comply with national tax regulations.
Many governments mandate e-invoicing for tax reporting and fraud prevention. These systems ensure real-time tax validation, automated VAT reporting, and compliance monitoring.
Examples:
- Italy (Sistema di Interscambio - SDI)
- India (GST E-Invoicing Portal)
- France (Chorus Pro for B2G transactions)
4. ERP-Integrated E-Invoicing Systems
Best for: Businesses using enterprise software for accounting, procurement, and financial operations.
ERP-based e-invoicing systems allow companies to generate, send, and process invoices within their enterprise software, ensuring seamless financial management.
Examples: SAP Ariba, Oracle NetSuite, Microsoft Dynamics 365.
5. Cloud-Based E-Invoicing Solutions
Best for: Businesses seeking flexible, automated invoicing without ERP dependency.
Cloud-based e-invoicing platforms offer automation, multi-channel invoice delivery, and real-time tracking. These systems suit SMEs and mid-sized businesses that need scalable and regulatory-compliant invoicing.
Examples: Bill.com, Basware, Tungsten Network, Parseur (for invoice data extraction & automation).
6. Supplier Network-Based E-Invoicing Systems
Best for: Businesses that exchange invoices frequently with a network of suppliers.
These platforms create centralized invoice hubs where suppliers submit invoices through a secure portal and businesses process them automatically.
Examples: Basware, Coupa, Ariba Network.
How does E-Invoicing work?
Electronic invoicing is a fully automated process that refines how businesses generate, send, receive, and process invoices. Unlike traditional invoicing, which often involves manual data entry, paper handling, and delayed approvals, it ensures seamless, real-time transactions between suppliers and buyers. Using standardized digital formats and secure transmission channels, businesses can improve efficiency, enhance compliance, and reduce operational costs. (Source: HighRadius)
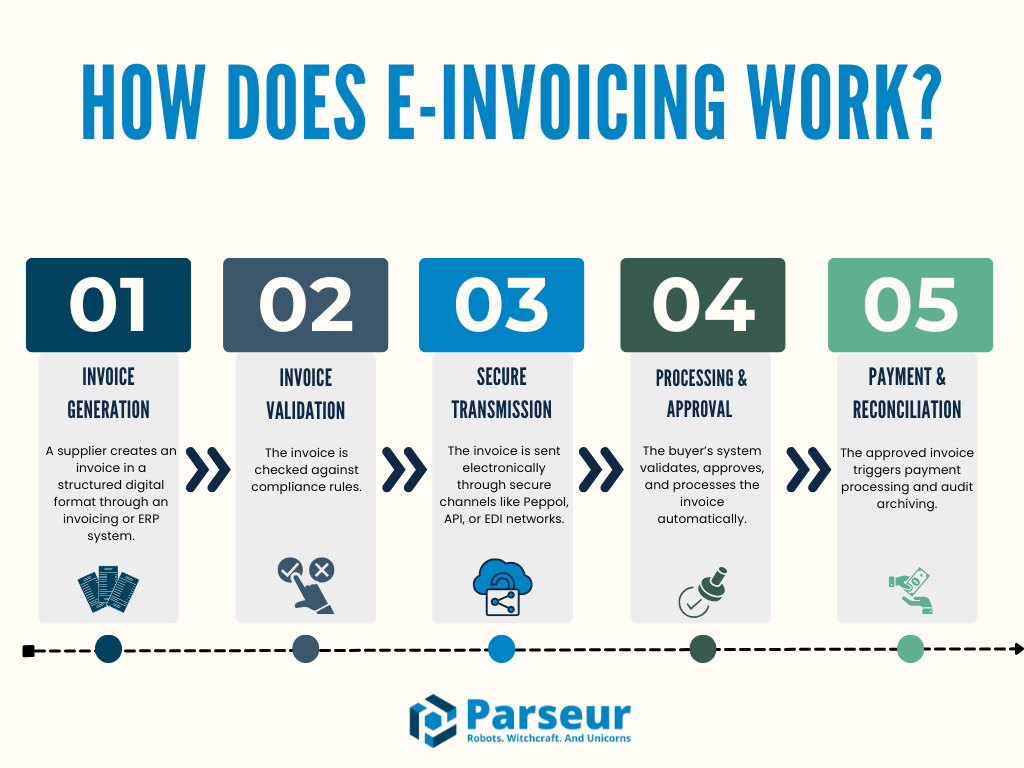
Here’s how the process typically works:
- Invoice generation – A supplier creates an invoice in a structured digital format through an invoicing or ERP system. (Source: Pagero)
- Invoice validation – The invoice is checked against compliance rules.
- Secure transmission – The invoice is sent electronically through secure channels like Peppol, API, or EDI networks.
- Invoice processing & approval – The buyer’s system automatically validates, approves, and processes the invoice.
- Payment & Reconciliation – The approved invoice triggers payment processing and audit archiving.
The growth of E-Invoicing
The shift from traditional paper and PDF-based invoicing to structured, electronic formats is driven by the need for greater efficiency, cost savings, and compliance with evolving tax regulations.
Government mandates such as VAT reporting requirements in the EU and GST are significant drivers. These mandates aim to reduce tax evasion and improve financial transparency. (Source: IMarc)
Digital transformation efforts in enterprises and SMEs. The increasing adoption of digital transformation enhances e-invoicing by automating manual processes, improving accuracy, accelerating invoice processing, and increasing efficiency and cost savings.
For example, in 2022, 70% of businesses across the EU achieved a foundational level of digital capability. The EU aims to have at least 80% of adults with essential digital skills by 2030. (Source: The Business Research Company)
- Reduction in tax fraud and increased financial transparency. E-invoicing helps governments reduce tax fraud and evasion by increasing transaction visibility. This enables tax agencies to collect more VAT taxes on sales transactions. (Source: Tipalti)
Benefits of E-Invoicing: Why make the switch?
Unlike paper-based or manually processed digital invoices, it automates the entire billing cycle, reducing human intervention and the risk of errors.
Here are some of the key benefits:
1. Cost savings
- Eliminates paper, printing, and postage costs
- Reduces manual data entry and errors
- Faster processing reduces labor costs
2. Increased efficiency
- Automates data capture and validation
- Speeds up approval workflows
- Faster payment cycles
3. Improved accuracy
- Reduces human errors in data entry
- Automated invoice matching
- Enhances compliance with regulatory requirements
4. Enhanced security
- Secure electronic transmission
- Reduces risk of fraud and data breaches
- Improves audit trails
5. Environmental sustainability
- Reduces paper usage
- Lowers carbon footprint
Global E-Invoicing regulations
As e-invoicing gains traction worldwide, governments and regulatory bodies are implementing frameworks to standardize digital invoicing and improve tax compliance. While some countries have fully enforced e-invoicing for business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-government (B2G) transactions, others are in the early stages of adoption.
E-invoicing in the United States
- The U.S. does not have a nationwide e-invoicing mandate, but it is gaining traction for B2B and B2G transactions.
- The Business Payments Coalition (BPC) is leading efforts to establish a universal e-invoicing framework.
- Federal agencies are adopting PEPPOL-based e-invoicing for procurement processes.
- IRS and state tax authorities are exploring real-time e-invoicing for tax reporting in the future.
E-invoicing in the European Union
- Directive 2014/55/EU mandates e-invoicing for B2G transactions.
- Countries like Italy, France, and Spain have mandatory B2B e-invoicing.
- Peppol is the standard network for e-invoice exchange.
- The ViDA (VAT in the Digital Age) initiative aims to expand real-time e-invoicing across the EU by 2028.
E-invoicing in the United Kingdom
- No mandatory e-invoicing, but government procurement. (Source: Qvalia)
- Making Tax Digital (MTD) promotes digital record-keeping and VAT compliance.
E-invoicing in Asia
- India – Mandatory e-invoicing for businesses exceeding INR 10 crores under GST.
- China – Uses the Golden Tax System (GTS) for invoicing and tax reporting.
- Singapore – Adopts the Peppol framework for B2B transactions.
- Japan – Introduced the Qualified Invoice System in 2023 for tax compliance.
Best practices for implementing E-Invoicing
Implementing e-invoicing can significantly improve efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure regulatory compliance.
By choosing the right tools, training teams, and aligning with regulatory requirements, businesses can ensure a smooth transition to a fully digital invoicing system.
- Choose the right software.
- Ensure it supports compliance, automation, and integration with ERP systems.
- Ensure compliance with local regulations
- Stay updated with country-specific e-invoicing laws.
- Integrate with accounting & ERP systems
- Use API-based solutions or Peppol e-invoicing networks.
- Train your finance team
- Educate employees on formats, compliance, and automation.
- Automate invoice validation & approval workflows
- Use AI-driven solutions to match invoices and detect fraud.
- Monitor & improve performance
- Track KPIs like processing time, error rates, and cost savings.
Best E-Invoicing software & platforms
Choosing the right solution is crucial for seamless integration with existing systems and ensuring compliance with evolving regulations. Implementing an effective solution can significantly reduce processing times; some companies have reported reducing invoice processing from several weeks to less than 48 hours.
(Source: Basware)
1. SAP Ariba – Best for enterprise E-Invoicing
- End-to-end invoice automation for large organizations.
- Complies with global regulations.
2. Basware – Best for global compliance & Peppol integration
- Automates invoice approvals and payment processing.
- Supports Peppol e-invoicing.
3. QuickBooks & Xero – Best for SMEs & startups
- Easy for small businesses.
- Integrates with banking and payment systems.
Future Trends in E-Invoicing
As businesses and governments continue to embrace digital transformation, e-invoicing is evolving beyond simple automation. This growth is attributed mainly to government mandates and digital transformation initiatives. As of January 2024, more than 19 countries mandate e-invoicing for all taxable transactions, with 49 countries requiring it for specific transactions. (Source: CSSA)
1. AI-Powered Invoice Processing
- Machine learning for fraud detection and real-time categorization.
2. Blockchain for Secure Transactions
- Uses smart contracts for tamper-proof invoicing.
3. Global Standardization & Interoperability
- Peppol & UBL becoming global standards.
4. Real-Time Tax Reporting & Compliance
- Governments enforce real-time invoice validation and e-audits.
Why E-Invoicing Is Already the Future of Business Transactions
E-invoicing is no longer a futuristic concept but a present-day necessity, transforming financial operations, minimizing tax fraud, and boosting efficiency on a global scale. By embracing structured electronic formats, your organization can unlock significant compliance advantages, realize substantial cost savings through automation, and simplify your invoicing process. (Source: See Burger)
How to Transition from Manual Invoicing to E-Invoicing
While e-invoicing is becoming the new standard, transitioning from manual invoicing is a gradual process. Not all clients and suppliers will adopt e-invoicing simultaneously, which means businesses must be prepared to handle both traditional and electronic invoices during the migration period.
- Identify Your Business’s Readiness
- Choose the Right E-Invoicing Platform
- Automate Invoice Data Extraction with Parseur
- Educate & Onboard Suppliers and Clients
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are all the questions answered about e-invoicing.
-
What is the difference between e-invoicing and digital invoicing?
-
Digital invoicing may still involve manual steps, while e-invoicing automates the entire process end-to-end, making it faster, more accurate, and compliant with global tax regulations.
-
Is e-invoicing mandatory in the U.S.?
-
E-invoicing is not mandatory across the U.S. for private businesses but is gaining adoption in specific sectors.
-
How does Peppol work?
-
Peppol (Pan-European Public Procurement OnLine) is a global e-invoicing framework that enables businesses and governments to exchange invoices securely and efficiently.
Last updated on