Key Takeaways:
- Document processing automates the extraction of structured data from emails, PDFs, images, and scanned documents, minimizing manual input and reducing human error.
- The process typically involves five core steps: document collection, classification, optical character recognition (OCR), data extraction, and system integration.
- Businesses that adopt document processing tools report significant time savings (up to 80%) and reduced processing costs across various departments, including finance, operations, and logistics.
Document processing refers to the method of capturing, organizing, extracting, and managing data from various documents, whether scanned, digital, or paper-based, to make the information usable and accessible. It plays a crucial role in streamlining workflows across various industries, including finance, healthcare, legal, and logistics.
Despite its importance, businesses often face significant challenges with traditional document processing: manual data entry is prone to errors, delays pile up due to inefficiencies, and costs can quickly escalate.
Forbes reported that approximately 80% of enterprise data remains untapped in the unstructured realm of human interactions and conversations.
This guide covers everything you need to know about document processing in 2026, from its basics to its benefits, key use cases, software selection tips, and future trends, such as Intelligent Document Processing (IDP). Whether you’re just starting or looking to optimize your current system, this article will help you make informed, strategic decisions.
What Is Document Processing?
Document processing involves converting unstructured data, such as scanned documents, PDFs, or images, into structured, usable data. This process allows organizations to store, search, analyze, and take action on the information within their documents.
There are two primary approaches:
- Manual Document Processing involves individuals reading and manually inputting data. This is time-consuming, error-prone, and often costly.
- Automated Document Processing, on the other hand, utilizes tools such as artificial intelligence (AI) and Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to extract and organize data with minimal to no human intervention.
For example:
- A company might manually enter invoice details into a spreadsheet, which can take hours and increase the risk of errors.
- With a document processing tool, the same invoice is scanned, and the system automatically extracts vendor name, due date, and amount, entering it into a database in seconds.
This same method applies to onboarding forms, purchase orders, shipping documents, and more, saving valuable time and improving accuracy.
Why is Document Processing Important?
Manual data entry may seem manageable on the surface, but over time, it drains resources, creates bottlenecks, and increases the risk of human error. Employees spend hours sifting through forms, entering data line by line, and double-checking accuracy, only to have mistakes slip through and cause delays or compliance issues.
The cost of this inefficiency is staggering.
BayInfotech reported that a mid-sized federal agency that handles over a million documents annually, including forms, invoices, and compliance paperwork. Employees spend up to 30% of their time on manual administrative tasks, such as data entry and document verification, resulting in thousands of lost work hours each year. The average error rate for manual data entry is approximately 1%, resulting in 10 errors per 1,000 entries, which can lead to costly delays and compliance risks.
In the private sector, financial services firms lose over £10 million yearly due to manual agreement processing, with 47% reporting financial losses tied to these inefficiencies, as stated by FSTech.
Detailed Breakdown: How Document Processing Works (Step-by-Step)
Understanding how document processing works helps illustrate why automation is so valuable. Here's a clear breakdown of each step in the workflow, along with practical examples you’ll find in real-world operations.
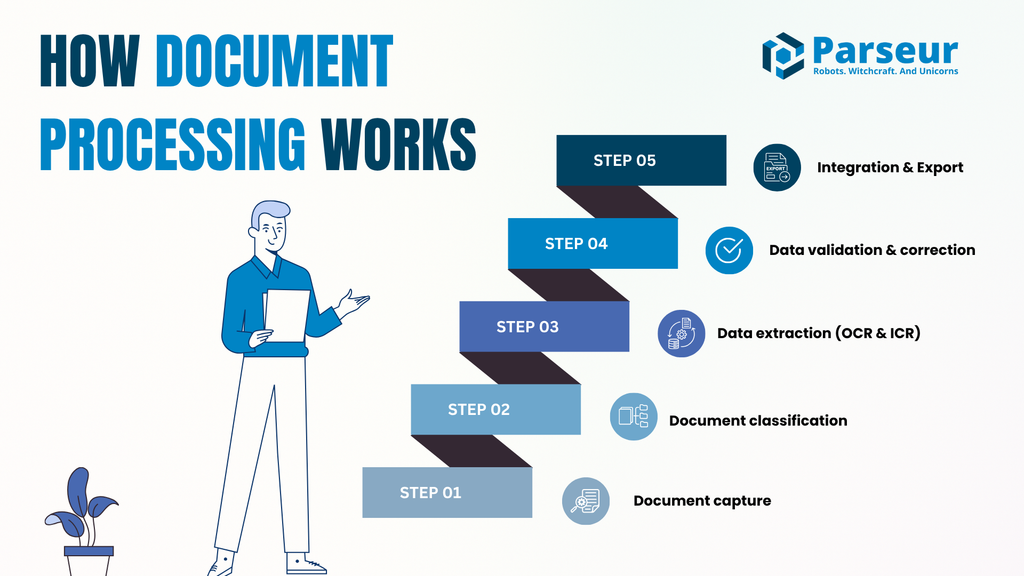
1. Document capture
The process begins by collecting documents from various sources. These can include:
- Scanned paper documents
- Email attachments
- Cloud storage (e.g., Google Drive, Dropbox)
Common document types processed include invoices, onboarding forms, purchase orders, medical records, and legal documents.
According to the AIIM 2024 Industry Watch Report: State of the Intelligent Information Management Practice, 72% of organizations agree that information management will become more critical in the next twelve months. The report highlights that a significant portion of enterprise data is unstructured, including scanned documents, email attachments, and files stored on cloud platforms such as Google Drive and Dropbox, making effective document capture essential. Organizations investing in AI and automation technologies for document capture are seeing improvements in productivity, compliance, and cost savings.
2. Document classification
Once captured, documents must be categorized correctly. This can be done through:
- Templates or rule-based logic
- AI-driven classification, which learns from document patterns to auto-label forms
Moreover, studies from Thesai show that machine learning algorithms, such as K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN), can achieve classification accuracies of up to 99.85%, with precision and recall rates approaching 100%, outperforming traditional manual and rule-based methods.
3. Data extraction (OCR & ICR)
- OCR (Optical Character Recognition) extracts printed or typed text.
- ICR (Intelligent Character Recognition) reads handwritten text—an advanced, AI-powered version of OCR.
Imarc stated that the global Optical Character Recognition (OCR) market size was valued at USD 13.95 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 46.09 billion by 2033, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.06% between 2025 and 2033. This growth is driven by increasing digitization, advancements in AI and machine learning, and a rising demand for automated data extraction across various industries, including finance, healthcare, and government.
Discover Parseur’s advanced AI OCR capabilities for document processing.
4. Data validation & correction
Once extracted, the tool validates the data using business rules (e.g., “invoice total must match line item sum”) or cross-referencing with databases.
There are two approaches:
- Fully automated validation for structured, consistent data
- Human-in-the-loop for reviewing low-confidence or flagged fields
Example:
In an accounts payable department, an automated system extracts invoice data and validates it against purchase orders using business rules such as “invoice total must match line item sum.” When a mismatch occurs, such as the invoice amount differing from the PO total, the system flags the document for human review. A team member then examines the flagged invoice to confirm or correct the data before approval, preventing costly payment errors or compliance issues.
According to Sama’s 2024 findings, AI models used out-of-the-box achieve around 50–70% accuracy in data validation tasks. However, when combined with a human-in-the-loop (HITL) validation process, accuracy improves dramatically to over 95%, ensuring higher data quality and significantly reducing costly errors.
5. Integration & Export
The final, structured data is exported in formats such as:
- CSV
- JSON
- Webhooks
- Real-time API connections to systems like CRMs or ERPs
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) Explained
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) is an advanced, AI-powered approach to document automation. It surpasses traditional OCR by integrating technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and computer vision to comprehend and extract data from PDF files and emails.
How is IDP different from traditional OCR?
| Traditional OCR | Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) |
|---|---|
| Extracts text from images or PDFs | Extracts contextual data and meaning |
| Struggles with unstructured layouts | Handles varying formats and document types |
| Rule-based and static | Learns and adapts over time through AI |
| Limited to printed/typed text | Works with handwritten notes, tables, and signatures |
A standard OCR tool might extract “Invoice No. 12345” as plain text, whereas IDP can recognize it as an invoice, extract key fields such as date, amount, and vendor, and even cross-check them against historical records.
IDP is ideal for industries handling high volumes of complex documents, such as finance, insurance, legal, and healthcare.
According to NextMSC, the global IDP market is experiencing significant growth. In 2023, it was valued at approximately USD 1.70 billion and is projected to reach USD 12.21 billion by 2030, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 32.5%.
Core Benefits of Automating Document Processing
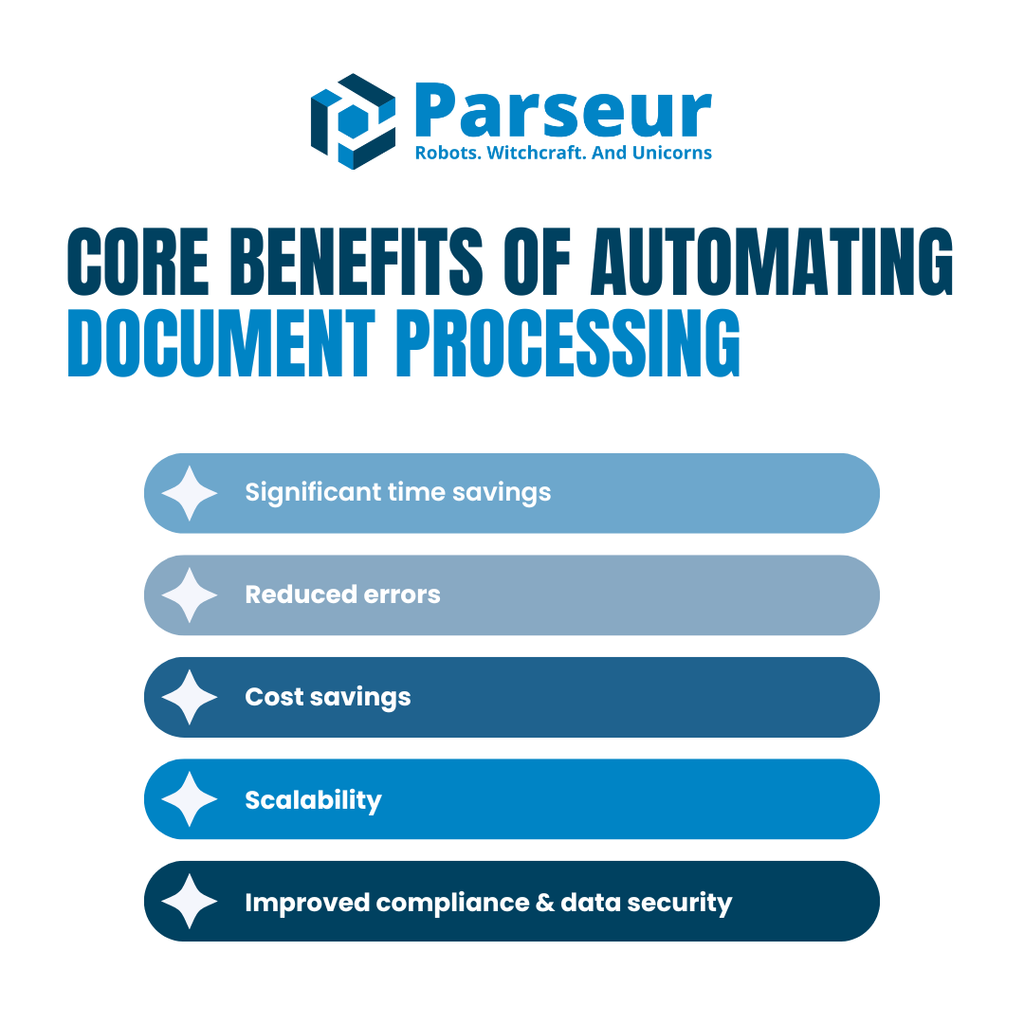
Automating document processing offers measurable improvements across various operational facets. Below are the core benefits, supported by real-world statistics and examples:
Significant time savings
Manual data entry is not only tedious — it’s a productivity drain. For example, manually parsing and inputting data from a single invoice can take anywhere from 5 to 10 minutes, depending on the complexity and formatting. Multiply that across hundreds or thousands of documents per month, and the time loss becomes substantial.
By automating tasks such as extracting invoice numbers, due dates, customer details, and total amounts from incoming documents, businesses can reclaim dozens of hours per employee each month. According to Zapier, businesses that automate routine tasks save an average of 4 to 6 hours per week per team member.
Reduced errors
Typos, misplaced fields, and duplicate entries are common with manual input. Document processing tools use rules, validation logic, and AI to ensure consistent, structured, and accurate data extraction, even from complex or unstructured formats.
💡 Parseur uses both template-based and AI-powered parsing to minimize error rates and flag inconsistencies before they impact your operations.
Cost savings
By automating document workflows, businesses reduce the need for manual labor, avoid costly rework due to errors, and accelerate turnaround times — all of which contribute to meaningful cost savings.
According to Deloitte, companies that utilize document automation achieve an average 24% cost reduction within the first year of implementation.
Scalability
As your business grows, the volume of documents increases. With manual processes, this leads to bottlenecks and hiring pressures. With automation, you can scale seamlessly without adding headcount.
Parseur processes thousands of documents daily without requiring technical setup or developer maintenance.
Improved compliance & data security
Whether it’s GDPR, HIPAA, or tax regulation, consistent data capture and traceability are essential. Document processing provides structured, timestamped records and logs, making compliance audits faster and more accurate.
Read about Parseur's GDPR compliance and privacy policy.
Use Cases of Document Processing
Document processing isn't limited to one industry or workflow. From finance and logistics to HR and customer service, businesses across various sectors are leveraging automation to streamline operations, eliminate manual data entry, and enable faster decision-making.
Invoice Processing & Accounts Payable Automation
Finance teams often receive hundreds of vendor invoices via email, each with a different format. Document processing automatically extracts key data points, such as invoice number, due date, total, and vendor name. Then, it routes the information to accounting software or ERPs, such as QuickBooks or NetSuite.
Logistics & Shipping Document Management
Shipping labels, delivery notes, and bills of lading come in various formats and layouts. With document processing, logistics teams can parse these documents, extract tracking number, customer information, and delivery details, and feed them into dashboards or fulfillment systems in real-time.
HR Onboarding & Document Collection
HR teams manage resumes, application forms, ID documents, and tax forms. Automating the extraction of candidate names, roles, and contact information streamlines the onboarding and employee record-keeping process.
Medical Forms & Patient Intake
Hospitals and clinics handle large volumes of intake forms, lab results, and discharge summaries. Document processing extracts critical fields, such as patient ID, symptoms, and medication, thereby improving speed and accuracy in healthcare workflows.
Legal & Compliance Document Review
Law firms and compliance teams process contracts, non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), regulatory filings, and case documents. Automation helps extract clause data, deadlines, and legal parties, streamlining internal review processes.
Email Parsing for Sales and Operations
Sales orders, lead capture forms, and customer support emails often include vital data that needs to be routed into CRMs, ticketing systems, or spreadsheets. Email parsing automates this flow by extracting structured data directly from email content and attachments.
Common Challenges in Document Processing (and Practical Solutions)
Despite its numerous benefits, document processing presents a set of challenges. Here's how organizations can overcome them with practical strategies:
OCR limitations and errors
Challenge: OCR engines may struggle with poor-quality scans, handwritten notes, or non-standard document layouts, leading to inaccurate data extraction.
Solution: Utilize advanced OCR, paired with machine learning or Intelligent Document Processing (IDP), to enhance recognition accuracy. Train models on specific document types, and apply validation rules to flag inconsistencies before integration.
Integration complexities
Challenge: Connecting document processing tools with existing systems (e.g., ERP, CRM, HR platforms) can be time-consuming and technically demanding.
Solution: Choose platforms that support APIs and offer pre-built integrations. Middleware tools or no-technical-knowledge platforms can help reduce custom coding and simplify deployment.
Privacy and security concerns
Challenge: Processing sensitive information (e.g., financial, health, or legal documents) raises concerns about data breaches and regulatory compliance.
Solution: Ensure the platform supports end-to-end encryption, audit trails, role-based access controls, and compliance with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA. Regular audits and employee training also reinforce data protection.
Change management and training issues
Challenge: Teams may resist new systems or lack the necessary skills to use them effectively, resulting in poor adoption.
Solution: Involve stakeholders early, provide hands-on training, and demonstrate a clear return on investment (ROI). Choose user-friendly platforms that don’t require deep technical expertise and offer ongoing support resources.
Choosing the Right Document Processing Tool
Selecting the right document processing tool is crucial for achieving effective automation. The right choice ensures accuracy, efficiency, and smooth integration with existing systems. Here are key factors to consider:
Accuracy
Look for tools with advanced OCR and machine learning capabilities that consistently extract data with high precision, especially from varied layouts or low-quality scans.
Ease of use
Platforms should offer a user-friendly interface and require minimal technical expertise. This ensures faster adoption and reduces reliance on IT teams.
Integration capabilities
Select tools that integrate seamlessly with your existing systems, such as ERP, CRM, or HR platforms, via APIs, webhooks, or third-party connectors.
Scalability
As your document volume grows, your tool should scale accordingly without significant performance drop-offs or cost surges.
Security and compliance
Opt for platforms that prioritize data privacy through encryption, role-based access, and compliance with standards like GDPR or HIPAA.
Why Choose Parseur?
Parseur stands out for organizations seeking a solution that requires no technical knowledge and is both powerful and easy to use. It allows users to:
- Automatically extract data from emails, PDFs, and other documents.
- Set up workflows without coding.
- Integrate with hundreds of apps through webhooks and tools like Zapier or Make.
- Benefit from high accuracy, rapid processing, and strong data security protocols.
Future Trends in Document Processing
As digital transformation accelerates, document processing is undergoing rapid evolution. Here are key trends shaping its future:
AI and Natural Language Processing (NLP) advances
Modern AI models paired with NLP are enabling systems to not only extract data but also understand context, sentiment, and intent, unlocking smarter automation and decision-making.
Cloud-Based API integration
Document processing is increasingly available through cloud APIs, allowing businesses to scale effortlessly, update capabilities instantly, and avoid on-premise infrastructure maintenance.
Real-Time document processing via mobile
With the improvement of mobile capture technologies, users can scan and process documents on the go, making it ideal for remote teams, field workers, and instant verification tasks.
Convergence with Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Document processing tools are being integrated into broader RPA workflows, allowing entire business processes (e.g., onboarding, claims handling) to be fully automated from start to finish.
Increased security & blockchain applications
To ensure tamper-proof records and traceable document histories, blockchain technology is being explored for document verification and secure digital signatures.
Conclusion
Document processing has evolved from a time-consuming, manual task into a highly efficient, automated solution that improves accuracy, saves costs, and boosts productivity. From OCR and intelligent classification to full-scale automation with IDP and RPA, businesses now have powerful tools to manage their documents at scale.
By understanding the full scope of document processing, from workflows and benefits to use cases and future trends, you’re better equipped to make strategic decisions for your organization.
Ready to enhance your operations?
Try Parseur today and experience document automation with no technical expertise required. Set up your workflows, integrate seamlessly, and start extracting data in minutes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are all the questions answered about document processing and automation.
-
What’s the difference between OCR and document processing?
-
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) is a technology that converts text from scanned images into machine-readable data. Document processing, on the other hand, is a broader workflow that may include optical character recognition (OCR) along with classification, validation, extraction, and system integration.
-
Do I need AI for document processing?
-
Not always. Basic workflows can rely on rules or optical character recognition (OCR). However, AI, especially Intelligent Document Processing (IDP), significantly improves accuracy and efficiency by handling complex layouts, handwritten text, and a wide range of document types.
-
Is document processing secure?
-
Yes. Reputable tools adhere to strict security protocols, including data encryption, access control, and compliance with standards such as GDPR and HIPAA. Cloud-based platforms may also offer audit logs and role-based permissions.
-
How accurate is automated document processing?
-
Accuracy depends on document quality, structure, and the tool used. Advanced platforms utilizing AI and OCR can achieve 90–99% accuracy, particularly when supplemented by human review or validation features.
-
Can document processing handle PDFs and attachments?
-
Absolutely. Most modern tools can extract data from PDFs, email attachments, scanned images, and even multi-page documents, making them versatile for day-to-day business needs.
Last updated on