Key Takeaways:
- Email parsers automatically extract structured data from emails and attachments, reducing manual entry and errors.
- They use rule-based templates or AI to identify and extract relevant information from email bodies, headers, and PDFs.
- Common use cases include processing orders, capturing leads, handling support tickets, and automating invoicing workflows.
- Most email parsers are no-code tools, making them accessible for non-technical users and easy to integrate with CRMs, spreadsheets, and databases.
Email parsing can be confusing if you’re new to it, especially with many tools, terms, and technical features floating around. That’s why we created this Email Parser FAQ, covering the 10 most common questions about email parsing to help you quickly understand how it works, why it matters, and how to get started.
According to a McKinsey study, employees spend an average of 28% of their workweek managing emails, which can seriously reduce time for more critical tasks.
Using an email parser to automate extracting important data from emails can help your team save weekly hours and reduce costly human errors. Whether you’re wondering what it is, how it compares to filters or rules, or how to extract data from emails and attachments, you’ll find clear, jargon-free answers below. Just scroll through to find the questions that matter most to you.
What Is an Email Parser?
An email parser is software that automatically extracts specific data from incoming emails. It transforms unstructured email content, such as text in the email body, headers, and even attachments, into structured data formats like CSV or JSON. This makes managing and using the information much easier, especially when integrating with other systems or databases.
An email extractor helps businesses automate repetitive tasks such as manual data entry, reporting, and workflow management by converting raw emails into organized data. Whether you need to capture order details, customer inquiries, or shipping information, an email parser ensures the data can be processed without manual effort. This ability to extract key information quickly and accurately is why many organizations rely on it to enhance communication and boost productivity.
How Does an Email Parser Work?
An email parser works by either monitoring an inbox or receiving forwarded emails. Once an email arrives, the parser scans the email body, headers, and sometimes attachments to identify the key information you need.
Parsers typically use pattern matching, custom templates, or AI-based methods. With rule-based parsers, you can define specific templates, keywords, or zones to tell the parser what to look for, such as names, dates, or invoice totals. Many tools also let you highlight examples directly in the email so the parser learns what to extract.
AI-powered parsers take a more flexible approach. Instead of relying on fixed rules, they understand the structure and content of the email to locate important information, even when formats vary.
Once the data is extracted, it can be sent to spreadsheets, CRMs, databases, or other applications using built-in integrations or APIs. This removes the need for manual copy-paste and speeds up your workflows.
What Are the Typical Use Cases for an Email Parser?
Email parsers are incredibly versatile tools used across many industries to automate data extraction from emails. Common use cases include processing orders, managing customer inquiries, extracting leads, and handling support tickets. By automating these tasks, businesses can save time, reduce errors, and improve overall workflow efficiency.
- Processing online order emails to capture purchase details quickly
- Capturing leads from contact forms without manual data entry
- Managing support tickets by organizing and routing customer requests
- Consolidating notifications from multiple sources into a single system
Any repetitive email containing structured information can be automated with an email parser to save time and reduce errors. For example, an e-commerce business might automatically update its inventory system from order confirmation emails, while a sales team can capture lead information directly from email submissions.
Customer support departments benefit by routing ticket data from emails into their helpdesk platforms. These examples highlight just how broadly this can be applied. For a deeper understanding of real-world applications, see our post on seven powerful email parser use cases for more detailed insights and examples.
Is an Email Parser the Same as an Email Filter or Rule (Like in Gmail/Outlook)?
Not exactly. While email filters and rules in popular email clients such as Gmail or Outlook can automatically sort, label, or forward emails based on keywords or sender addresses, they do not extract or organize data from the content inside the emails. These filters are designed to help manage your inbox by moving messages to folders or flagging them. Still, they do not pull specific information from the email body, headers, or attachments.
An email parser, on the other hand, goes beyond simple sorting. It reads the content of incoming emails to identify and extract key information such as order numbers, contact details, or invoice amounts. This extracted data is converted into structured formats like CSV or JSON, making it easy to use in other software systems or workflows.
In short, it provides a powerful, data-focused solution for automating information extraction, whereas filters and rules only organize your emails within the inbox. This distinction is important for anyone wondering if built-in email filters are enough, highlighting the added value an email processor brings to your automation toolkit.
Do I Need Coding Skills to Use an Email Parser?
Generally, no. Most modern email parser tools are designed with non-programmers in mind, featuring intuitive, user-friendly interfaces that allow you to simply click on the parts of the email text you want to extract. Many parsers also use AI technology to automatically identify and pull key data without requiring manual rule setup. For most use cases, you will not need to write any code, scripts, or complex formulas to get started with email parsing.
That said, some advanced users may choose to extend the capabilities of their tool by using regular expressions (regex) or custom scripts for more precise or complex data extraction needs. However, these options are entirely optional and not required for typical use. This design makes email parsing accessible to business owners and teams who want to automate data extraction without technical barriers.
Most of it requires no coding, and setting up a parsing rule is usually straightforward and quick. For those interested in how AI and templates differ in parsing, you can explore our article comparing AI vs rule-based email parsers for more details.
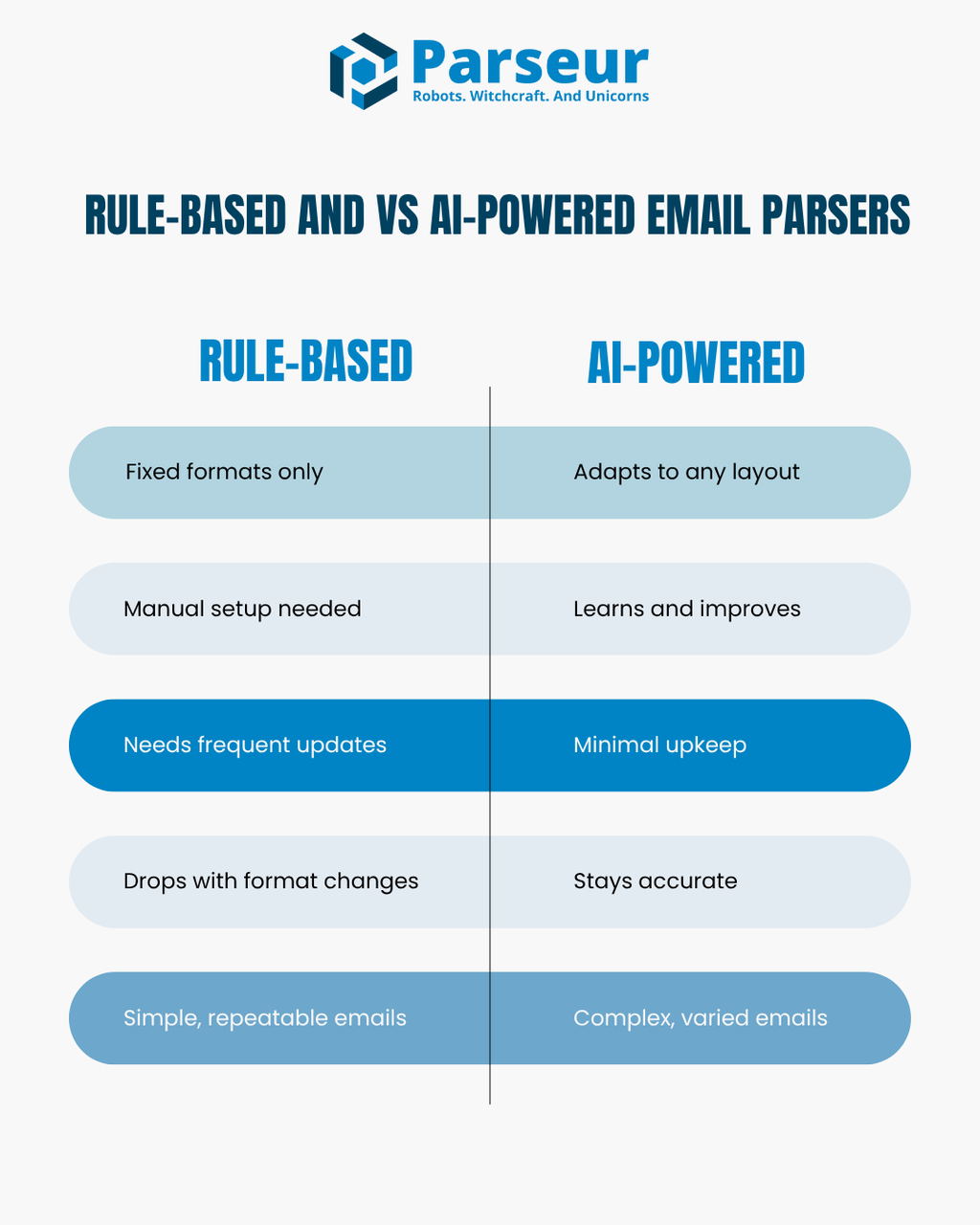
What’s the Difference Between Rule-Based and AI-Powered Email Parsers?
Rule-based parsers rely on predefined templates or keywords to extract data, working well when emails follow a consistent format. AI-powered parsers use machine learning to understand context and patterns, adapting to different email layouts and accurately extracting data.
How Do I Set Up an Email Parser?
Setting up an email parser is easier than you might think, even if you’re not tech-savvy. With just a few steps, you can automatically extract important data from your emails to simplify your daily tasks.
Let’s take the example of Parseur where the setup typically involves:
- Creating a free account on Parseur.
- Forward your emails to Parseur.
- Parseur extracts email data automatically.
- Parsed data can be downloaded or sent to any application of your choice.
Are Email Parsers Safe to Use?
Yes, email parsing tools such as Parseur take security and privacy very seriously. Using an email parser is no less secure than handling email typically, as long as the tool follows strong security practices. They usually use encryption, such as HTTPS, to protect your data during transmission and store information securely on their servers. This means the data extracted from your emails is handled with strong safeguards to prevent unauthorized access.
Considering that Egress stated that 94% of organizations have fallen victim to phishing attacks in the last 12 months, choosing a trusted and well-established provider is crucial. Look for clear privacy policies, compliance with regulations like GDPR, and strong security features.
If your emails contain highly sensitive information, check if the parser offers additional protections such as on-premise deployment or data redaction options. Always ensure you have permission to process any personal or sensitive data in your emails.
Can an Email Parser Handle Attachments and PDFs?
Many email parsers can parse attachments such as PDFs, Word documents, and Excel files. They use advanced AI OCR to extract data from different types of documents and images.
Why Should I Use an Email Parser Instead of Doing Data Entry Manually?
An email parser can save you significant time and help eliminate human error. Manually reading emails and typing data into your system is time-consuming and prone to mistakes like typos or missed information. An email parser automates this process by extracting the data quickly and accurately, handling large volumes of emails without fatigue or inconsistencies. This means your business can maintain data accuracy and improve overall efficiency.
Another major benefit is scalability. Imagine receiving hundreds of order confirmations or support requests in a single day. While you might struggle to keep up and become overwhelmed, this can process all those emails instantly and without delay. This boosts productivity and frees your team to focus on higher-value tasks like customer service or strategic planning.
Conclusion
If you didn’t find exactly what you were looking for, feel free to reach out—we’re happy to help you get the answers you need. Now that you’ve explored some of the most common questions about email parsing, why not experience it yourself? You can try Parseur for free and see how it effortlessly extracts data from your emails, saving you time and reducing errors.
Last updated on




