Key Takeaways
- KIE goes beyond OCR by extracting and understanding meaningful fields, not just raw text.
- Businesses save up to 70% in processing costs and reach 98% accuracy with AI-powered data extraction.
- Intelligent document processing adoption is surging, with the market projected to exceed $12.35 billion by 2030.
- Parseur delivers practical KIE with template-free, adaptable automation that integrates directly into your workflows.
Businesses face a flood of unstructured data, invoices, contracts, medical forms, and customer records. Manually entering this information into systems is slow, error-prone, and costly, leaving teams buried in repetitive tasks instead of focusing on higher-value work.
This is where Key Information Extraction (KIE) comes in. KIE uses document processing AI to automatically identify and capture essential fields (like names, totals, or dates) from documents. As part of Intelligent Document Processing (IDP), it transforms messy data into clean, structured insights that businesses can act on immediately.
Finance, healthcare, logistics, and legal organizations are already adopting KIE to cut costs, reduce errors, and accelerate operations. Furthermore, AI is simplifying daily tasks, with 75% of marketers reporting that AI simplifies their job responsibilities, according to Elfsight. By automating repetitive processes such as scheduling posts, segmenting audiences, or running A/B tests, professionals free up more time for creative and strategic work. In the same way, KIE removes the manual burden of data entry, allowing teams to focus on high-value decision-making and customer engagement.
In this guide, we’ll explain KIE, how it works, and where it delivers the most impact, so you can see why it’s becoming a must-have in modern document workflows.
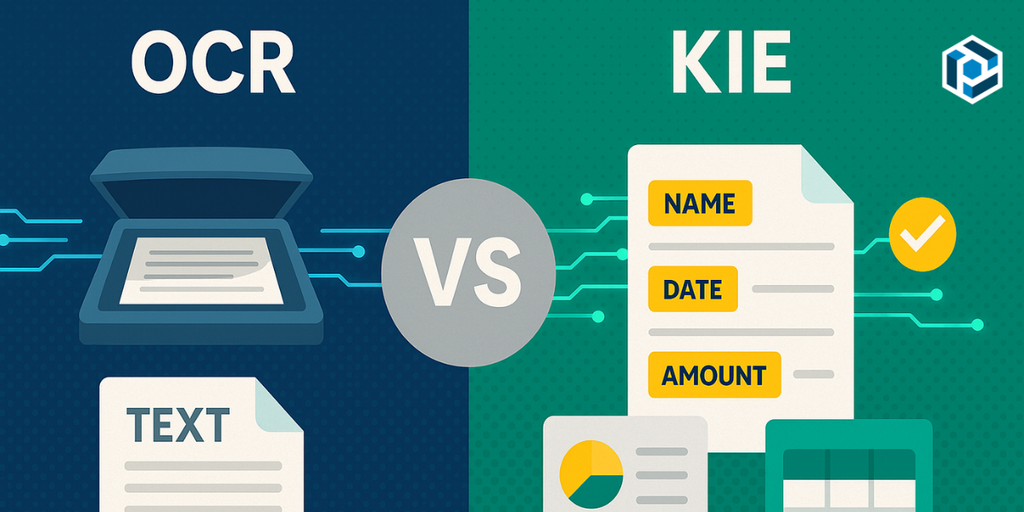
What Is Key Information Extraction (KIE)?
Key Information Extraction (KIE) is automatically identifying and extracting essential data fields from documents. In 2025, KIE plays a pivotal role in the rapidly expanding intelligent document processing (IDP) market, which is projected to grow at a compound annual rate of 32.18%, reaching a forecast of USD 49.7 billion by 2035 based on Spherical Insights.
Unlike traditional OCR (Optical Character Recognition), which only converts images of text into machine-readable text, KIE goes a step further and understands meaning and context.
For example, KIE doesn’t just read numbers; it recognizes whether a figure is an invoice total, a contract date, a customer name, or a purchase order number. This makes it a cornerstone of AI-powered data extraction and a key capability within intelligent document processing (IDP).
In short, KIE means turning raw, unstructured documents into structured, actionable data that businesses can use for faster decisions and more efficient workflows.
How Does KIE Work? (Step-by-Step)
The Key Information Extraction (KIE) process is a multi-layered workflow that transforms raw, unstructured text into clean, structured, and actionable data. Instead of just “reading” text, KIE understands context, identifies important fields, and delivers data in a format that can be directly used in business systems.
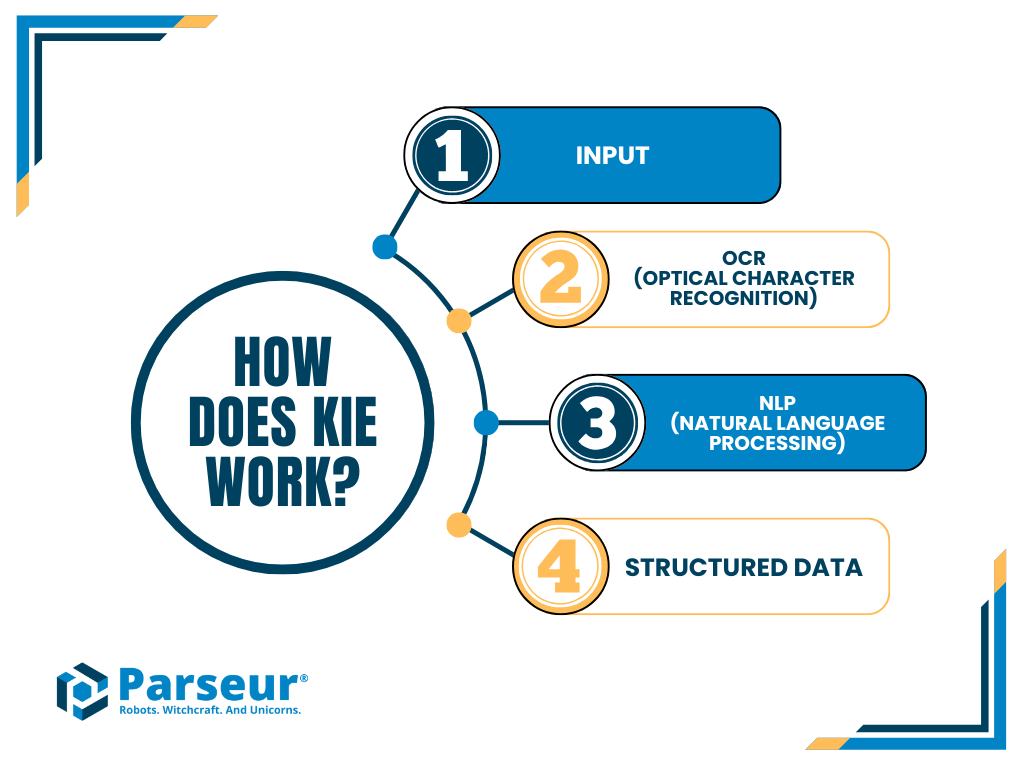
Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
Step 1. OCR (Optical Character Recognition)
The first step is to capture text from documents. OCR scans images, PDFs, or handwritten notes and converts them into machine-readable characters. This step ensures that even non-digital documents (like scanned invoices or forms) can be processed.
Step 2. Natural Language Processing (NLP) & AI models
After the text is captured, NLP and AI algorithms analyze it to determine meaning and context. Unlike raw OCR, which only “sees words,” this stage identifies how those words relate. For example, in an invoice, NLP can distinguish between a company name, a billing address, and a line item.
Step 3. Entity recognition
At this stage, the system pinpoints and tags specific fields of interest. This is where key data extraction truly happens, pulling out the information businesses need most.
Examples include:
- Invoice number
- Customer or supplier names
- Dates (issue date, due date)
- Financial amounts (subtotal, tax, total)
Step 4. Validation & formatting
Extracted data isn’t just copied; it’s verified and standardized for accuracy. Once verified, the structured data is automatically pushed into downstream systems such as CRMs, ERPs, accounting tools, or analytics dashboards.
For instance:
- Dates are reformatted into a consistent format (MM/DD/YYYY or YYYY-MM-DD).
- Phone numbers and currency symbols are normalized.
- Errors like duplicate entries or missing fields are flagged.
By combining OCR, NLP, and AI-driven entity recognition, key information extraction (KIE) ensures businesses get high-quality, actionable data without the bottlenecks of manual entry.
KIE vs OCR vs IDP: What’s The Difference?
When discussing document processing AI, it’s easy to confuse OCR, KIE, and IDP. While they’re related, each serves a different purpose in the automation pipeline:
- OCR (Optical Character Recognition): Converts scanned documents or images into machine-readable text. Example: turning a paper invoice into digital text.
- KIE (Key Information Extraction): Goes beyond OCR by identifying and extracting specific, meaningful fields such as invoice totals, contract dates, or customer names.
- IDP (Intelligent Document Processing): The full automation stack. It combines OCR + KIE + validation + integrations, ensuring extracted data flows directly into business systems like ERPs, CRMs, or databases.
Think of it like this:
- OCR = “I can read.”
- KIE = “I can understand and extract key details.”
- IDP = “I can automate the entire process from reading to exporting structured data.”
This makes KIE a core component of intelligent document processing (IDP), bridging the gap between raw text recognition and actionable data extraction.
KIE vs OCR vs IDP: functions, use cases, and complexity
| Factor | OCR (Optical Character Recognition) | KIE (Key Information Extraction) | IDP (Intelligent Document Processing) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core Function | Converts scanned or imaged text into machine-readable characters. | Extracts specific, meaningful fields (e.g., invoice total, contract dates). | End-to-end automation: OCR + KIE + validation + integrations. |
| Level of Understanding | Reads text only (“I can read”). | Understands context and extracts structured data (“I can understand”). | Complete automation workflow (“I can automate”). |
| Examples | Scanning a paper invoice into editable text. | Identifying invoice numbers, totals, and supplier names. | Reading invoices, extracting totals, validating accuracy, and exporting into ERP/CRM. |
| Use Cases | Digitizing paper archives, searchable PDFs. | Invoice data extraction, contract automation, and forms processing. | Accounts payable automation, claims processing, and end-to-end document workflows. |
| Complexity | Low – simple text recognition. | Medium – requires AI/NLP models. | High – combines multiple AI layers with business system integrations. |
| Output | Plain text. | Structured, usable data fields. | verified, formatted data flowing into downstream systems. |
Why Is KIE Important? (Statistics & Market Trends)
According to the survey conducted by Parseur in partnership with Question Pro, manual data entry remains one of the costliest inefficiencies in modern business. U.S. companies spend an average of $28,500 per employee annually on manual data entry, amounting to millions or billions for large organizations. This is where Key Information Extraction (KIE) delivers measurable impact.

- Cost savings: Automated document processing tools achieve 60–80% cost reduction compared to manual entry methods, according to Paperarchive.** For example, OCR-based systems have been found to cut processing costs significantly.
- Accuracy boost: Advanced document AI systems, when paired with KIE methods, deliver up to 98% accuracy in extracting structured fields—dramatically reducing human error. A real-world scenario showed 98% field-level accuracy versus 95–97% manually, as stated by Jordan N.
- Market growth: The global Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) market, which relies heavily on KIE, is projected to grow from around $2.30 billion in 2024 to approximately $12.35 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 33.1%.
- Adoption surge: According to Global Growth Insights, over 65% of enterprises are expected to fully integrate IDP solutions into their workflows by 2034.
The takeaway: KIE isn’t just a convenience; it’s becoming a competitive necessity. Businesses that adopt KIE gain faster operations, lower costs, and more reliable data to power decision-making.
Real-World Applications Of KIE
Key Information Extraction (KIE) isn’t just a buzzword; it solves everyday business problems across industries. By turning unstructured documents into structured insights, document processing AI helps organizations cut manual effort and speed up operations.
- Invoices & Receipts – Automate invoice data extraction, pulling out supplier names, totals, taxes, and payment dates for accounting systems.
- Contracts – Identify and extract key terms such as contract dates, parties, renewal periods, and obligations, reducing legal review times.
- Forms – Capture patient information, claim numbers, or customer onboarding data directly from forms, simplifying workflows in healthcare and insurance.
- Logistics – Extract critical details from bills of lading, shipping manifests, and delivery receipts, improving supply chain visibility.
By applying AI data extraction to these scenarios, businesses eliminate repetitive copy-paste work and gain faster, more accurate access to the data that drives decision-making.
How LLMs Boost Key Information Extraction
Large Language Models (LLMs) are redefining what’s possible in Key Information Extraction (KIE). Traditional KIE relies on a combination of OCR and NLP models to identify key fields, but LLMs take it a step further by bringing deeper contextual understanding and adaptability.
Here’s how LLMs improve KIE:
- Contextual Accuracy: LLMs translate meaning based on context instead of just spotting keywords. For example, they can distinguish between a billing address and a shipping address or identify which date refers to an invoice due date rather than an issue date.
- Template-Free Extraction: Traditional KIE tools often struggle with unseen layouts. LLMs adapt more flexibly, extracting data from documents with varied formats such as invoices, contracts, receipts, or medical forms without rigid templates.
- Multilingual Capability: With their training across multiple languages, LLMs can extract key information from global documents, making them highly effective in industries like logistics, finance, and healthcare that work across borders.
- Reasoning & Cross-Field Validation: LLMs can “reason” across data fields, for example, checking if the total amount equals line-item sums, or if a contract’s start and end dates make sense. This reduces errors that traditional models might miss.
- Versatility & Continuous Learning: Since LLMs are pre-trained on massive datasets, they can quickly adapt to new document types with minimal fine-tuning, making KIE more flexible for enterprises handling millions of records.
Why it matters:
By integrating LLMs into document processing AI, businesses get higher accuracy, fewer exceptions, and a faster launch. This progress bridges the gap between raw text capture and accurate intelligent document processing (IDP).
Traditional KIE vs. KIE Powered by LLMs
| Factor | Traditional KIE (OCR + NLP) | KIE with LLMs |
|---|---|---|
| Layout Handling | Needs templates or training per document type | Works across diverse, unseen formats |
| Context Awareness | Limited (keyword or rule-based) | Deep contextual understanding of fields |
| Multilingual | Usually requires language-specific models | Supports multiple languages natively |
| Error Reduction | May miss inconsistencies or cross-field checks | Can verify totals, dates, and relationships logically |
| Adaptability | Slower adaptation to new document types | Rapid scaling with minimal fine-tuning |
Challenges In KIE (How Tools Solve Them)
Key Information Extraction (KIE) comes with challenges like any advanced technology. Real-world documents are rarely uniform, and traditional OCR limitations often fall short when businesses need accuracy at scale. Common hurdles include:
- Unstructured layouts – Invoices, receipts, and contracts come in hundreds of formats, making it difficult for rigid systems to capture the right fields consistently.
- Multilingual documents – Global businesses must extract data across multiple languages and writing systems.
- Low-quality scans – Faded print, skewed images, or handwritten notes can reduce accuracy.
- Flexibility for enterprises – Processing millions of documents reliably requires strong infrastructure and automation.
Modern document AI tools combine OCR, machine learning, and NLP to deliver intelligent document processing (IDP) that adapts to diverse layouts, imperfect scans, and multilingual inputs with 90–99% accuracy, based on Parseur’s 2026 benchmarks. By blending AI-powered and template-based parsing, Parseur enables fast AI data extraction for developers and non-technical teams, eliminating the need for custom workflows.
This combination of flexibility and precision makes KIE solutions like Parseur powerful and practical for real-world business needs. Beyond just extracting text, they ensure that data is accurate, reliable, and immediately usable, laying the foundation for true automation at scale.
According to Forbes, its cloud-based platform scales to process thousands of documents daily, reducing automated data entry time by up to 80% compared to manual methods. This level of invoice data extraction accuracy and adaptability ensures compliance with GDPR while powering faster, error-free decision-making across finance, logistics, healthcare, and customer service.
Traditional OCR vs. Modern KIE tools
| Factor | Traditional OCR | Modern KIE (e.g., Parseur) |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Reads raw text only | Extracts context-rich, structured fields |
| Layouts | Struggles with varied templates | Learns and adapts to different formats |
| Languages | Limited language support | Handles multilingual documents |
| Adaptability | Slow and resource-heavy | Built to scale with enterprise workflows |
| Usability | Developer-heavy setup | API + web app for both devs & ops teams |
Modern AI data extraction platforms transform what was once a rigid process into a flexible, adaptive system, bridging the gap between manual data entry and enterprise-ready automation.
How Parseur Fits Into KIE
When businesses look for a practical way to apply Key Information Extraction (KIE), Parseur offers a proven, AI-powered solution. Rather than just reading text, Parseur’s AI data extraction engine understands and organizes information across a wide range of document types, from invoices and receipts to contracts and forms.
Unlike rigid, template-based systems, Parseur is template-free, meaning it adapts to different layouts with minimal setup. This makes it easier for teams to process documents without constantly rebuilding rules or templates.
Parseur also integrates seamlessly with accounting platforms, ERPs, and CRMs, and sends extracted data directly into business workflows. Whether you’re handling a few hundred documents a month or scaling to millions, Parseur combines adaptability with ease of use.
In short, Parseur delivers the practical side of KIE in document processing: accurate extraction, simple integration, and enterprise-ready automation.
Future of KIE: AI, LLMs, And Beyond
Rapid advances in AI and large language models (LLMs) are shaping the future of key information extraction (KIE). Where early systems relied on rigid templates and rules, the next wave of document processing AI is moving toward fully AI-driven extraction that understands context, intent, and industry-specific nuances.
Key trends shaping the future include:
- LLMs for data extraction – Foundation models improve accuracy by translating complex layouts, ambiguous text, and handwritten inputs.
- Real-time document processing – Businesses will demand instant insights as documents arrive, not hours or days later.
- Multimodal AI – Combining text, images, and even voice inputs to handle diverse document formats.
- Industry-specific compliance – From finance to healthcare, regulatory alignment will remain central, ensuring extracted data is both accurate and lawful.
At Parseur, the roadmap aligns with these changes: expanding AI capabilities, integrating with Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) ecosystems, and ensuring adaptive, compliant, and future-ready automation.
The takeaway? The future of KIE is not just about reading documents; it’s also about understanding them with human-like accuracy, at enterprise scale.
Why Now Is The Time To Embrace KIE
Key Information Extraction (KIE) has moved from being a “nice-to-have” to an essential part of modern document processing. By transforming messy, unstructured documents into clean, structured insights, KIE saves businesses time, reduces errors, and creates room for higher-value work. With accuracy rates of up to 98% and cost savings of 60-80%, it’s clear why organizations across finance, healthcare, logistics, and legal are making KIE central to their digital strategy.
That’s where Parseur comes in. As an AI-powered data extraction platform, Parseur brings KIE to life with a flexible, template-free engine that adapts to any document format. From invoices to contracts and beyond, Parseur ensures your data flows seamlessly into the systems you already use, without the manual grind.
Ready to see it in action? Try Parseur for free today and experience how KIE can transform your document workflows.
Frequently Asked Questions
Key Information Extraction (KIE) transforms how businesses handle documents, but many still question its capabilities, applications, and how it differs from related technologies. Below, we answer the most common questions to help you understand KIE and see how tools like Parseur make intelligent document processing easy and dynamic.
-
What is Key Information Extraction (KIE)?
-
KIE automatically identifies and extracts essential data fields from documents, turning unstructured text into structured, actionable data. Unlike OCR, KIE explains context and meaning, such as recognizing invoice totals, contract dates, or customer names.
-
How is KIE different from OCR?
-
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) converts text from scanned documents or images into machine-readable characters. KIE goes further by understanding the context and extracting specific, meaningful fields from that text.
-
How does KIE fit into Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)
-
IDP is the full automation workflow: it combines OCR, KIE, validation, and integrations. KIE is the core component, bridging the gap between raw text recognition and actionable insights, enabling automated data entry into CRMs, ERPs, and other systems.
-
What types of documents can KIE handle?
-
KIE can process invoices, receipts, contracts, forms, shipping manifests, medical records, and virtually any structured or semi-structured document.
-
How accurate is KIE?
-
Modern KIE solutions, like Parseur, extract key fields with up to 98% accuracy, drastically reducing human error and the need for manual data entry.
-
Can KIE handle multiple languages and formats?
-
Yes. With AI-powered models and LLM integration, KIE can adapt to different layouts, languages, and even handwritten or low-quality scans, making it suitable for global operations.
-
How does Parseur put KIE into action?
-
Parseur offers a template-free, AI-powered engine that extracts structured data from any document format. It integrates with CRMs, ERPs, and cloud-based workflows, scaling from hundreds to millions of documents with minimal setup.
-
Why should businesses adopt KIE now?
-
With growing document volumes, rising labor costs, and competitive pressure, KIE saves time, reduces errors, and enables faster decision-making. The IDP market is expected to exceed $12.35 billion by 2030, reflecting widespread adoption.
Last updated on