Master data is the core set of shared business entities, such as customers, products, and suppliers, used across systems to standardize reporting and operations. It’s the consistent “who” and “what” your organization relies on daily, ensuring every team works from a single, trusted source of truth.
Key Takeaways:
- Master data defines the core entities that maintain business systems' consistency and alignment.
- Clean, unified master data improves reporting accuracy, customer experience, and compliance.
- At Parseur, we help organizations simplify document data capture, enabling cleaner master data and more reliable automation.
Master data is the foundation of accurate business operations. It maintains critical information, such as customers, products, and suppliers, consistently across all systems, allowing teams to make informed decisions using the same facts. In this article, you’ll find a clear definition of master data, simple examples from common business domains, and quick answers to frequently asked questions to help you understand why it matters for every organization.
Simple Definition
Master data refers to the key business information that defines the core entities your organization relies on every day, such as customers, products, suppliers, and employees. It serves as the single source of truth, keeping all systems aligned and consistent. In practice, Master Data Management (MDM) combines processes and technology to maintain a golden record, the most accurate, up-to-date version of each business entity shared across departments and applications. Globally, the master data management market is valued at $18.63 billion in 2025, according to Fortune Business Insights.
Top Master Data Domains
Master data typically falls into a few core domains that describe the most important entities shared across business systems. Each domain provides a single source of truth, supporting consistent reporting, analytics, and operational efficiency.
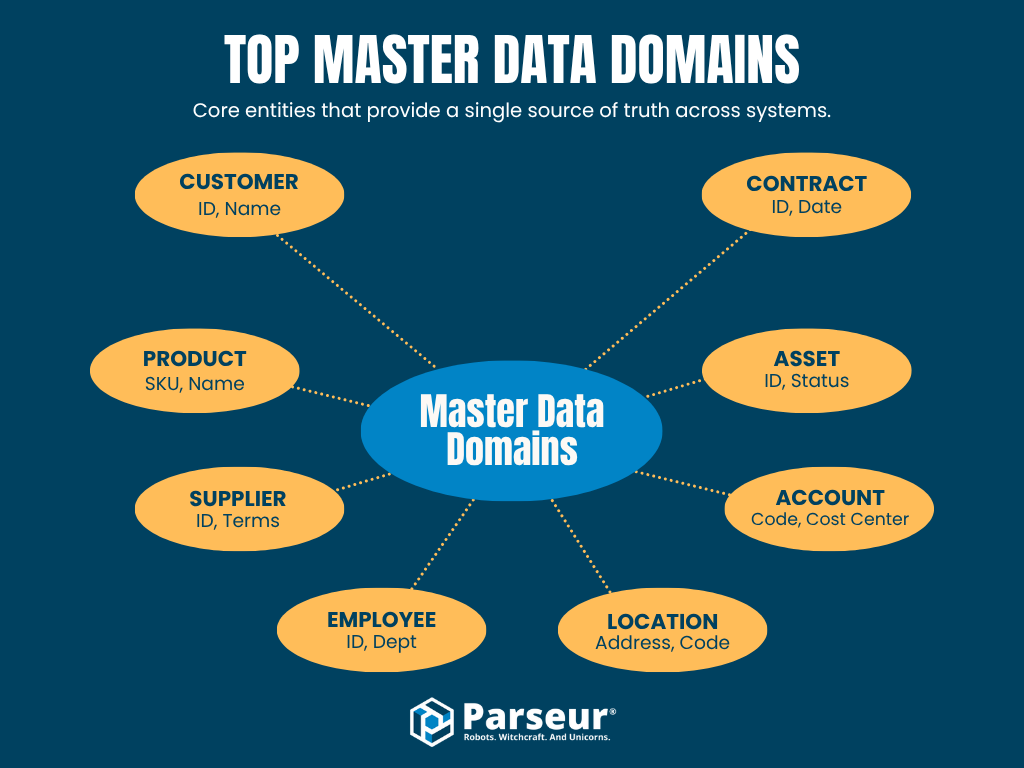
Below is a summary of the most common master data domains, their definitions, typical source systems, and example fields.
| Domain | Definition | Typical Source Systems | Common Fields |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer | Information about people or organizations that buy or use your products. | CRM, Billing, Support | Customer ID, Company Name |
| Product | Core data describing goods or services sold. | ERP, PIM, E-commerce | Product Name, SKU |
| Supplier/Vendor | Data about external providers of materials or services. | ERP, Procurement, AP | Supplier ID, Payment Terms |
| Employee | Details of internal staff and organizational roles. | HRIS, Payroll, Active Directory | Employee ID, Department |
| Location. | Information about physical or virtual sites used in business operations. | ERP, Facilities, GIS | Address, Site Code |
| Account (Chart of Accounts) | Structure used for organizing financial transactions. | ERP, Accounting, Finance Systems | Account Code, Cost Center |
| Asset | Records of owned or leased equipment, software, or infrastructure. | Asset Management, ERP | Asset ID, Status |
| Contract | Agreements defining relationships with customers, vendors, or partners. | CLM, ERP, CRM | Contract ID, Effective Date |
Each of these domains forms part of a company’s data foundation. Consistently managing them reduces duplication, ensures data accuracy, and enables analytics teams to build trusted insights from a unified data model.
Master Data vs Transactional vs Reference Data
Master data defines the core business entities, such as customers, suppliers, or products. Transactional data records what happens between them, like orders, invoices, or payments. Reference data provides standardized values that describe or categorize both master and transactional data, such as country codes or currency types.
Together, these three data types form the backbone of enterprise information management: master data provides stability, transactional data drives activity, and reference data ensures consistency across systems.
Based on Grandview research, the global enterprise data management market reached $110.53 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a 12.4% CAGR through 2030. This growth reflects how organizations are prioritizing reliable, unified data to support automation, AI, and real-time decision-making. As cloud adoption and data volume accelerate, companies are investing heavily in MDM and governance frameworks to reduce duplication, ensure compliance, and improve analytics accuracy.
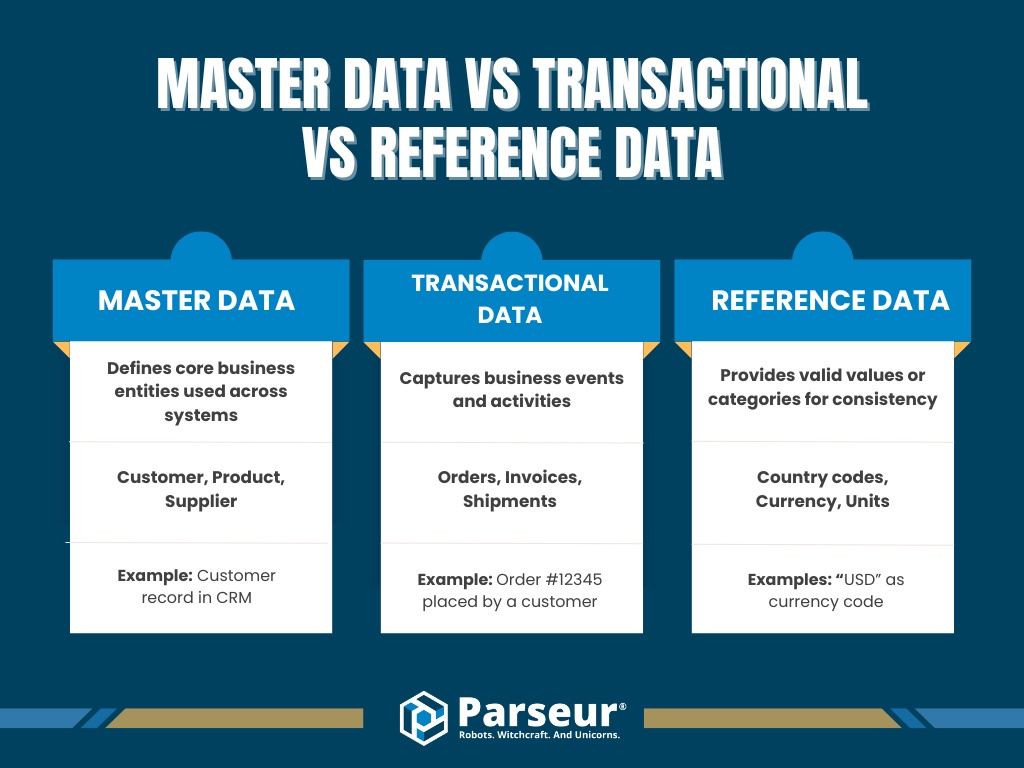
Quick Comparison Table
| Data Type | Purpose | Example Entities | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Master Data | Defines core business entities used across systems | Customer, Product, Supplier | Customer record in CRM |
| Transactional Data | Captures business events and activities | Orders, Invoices, Shipments | Order #12345 placed by a customer |
| Reference Data | Provides valid values or categories for consistency | Country codes, Currency, Units | “USD” as currency code |
Why Master Data Matters (Business Impacts)
Master data is the foundation of reliable operations and analytics. When it’s clean, consistent, and shared across systems, every department works from the same facts, which improves efficiency and decision-making.
- Accuracy & consistency: A unified customer or product record eliminates duplicate entries and reduces data errors across departments.
- Reliable reporting: Consistent master data ensures that finance, sales, and operations report from the same numbers and no more mismatched KPIs.
- Better customer experience: Accurate customer master data enables personalized support and seamless cross-channel interactions.
- Compliance & governance: Standardized entity data helps meet audit, tax, and privacy regulations with less manual effort.
- Automation & AI readiness: Clean, structured master data is essential for reliable automation, analytics, and machine learning.
- Illustrative example: A shared product master can reduce order errors and returns by maintaining consistent SKUs and descriptions across sales and fulfillment systems.
How Master Data Is Used Across Systems
Master data connects the core systems that run a business, ensuring every application uses consistent, verified information. It acts as the bridge between daily operations and strategic insights.
- CRM: Uses customer master data to manage relationships, track history, and personalize interactions.
- ERP: Relies on product, supplier, and account masters to simplify purchasing, inventory, and financial processes.
- Billing & Finance: References customer and contract master data to generate accurate invoices and recognize revenue correctly.
- BI & Analytics: Combines standardized master data to deliver consistent metrics and dashboards across the organization.
- AI & ML Pipelines: Depend on clean, structured master data to train accurate models and automate decision-making.
Master Data: The Foundation of Reliable Business Operations
Master data provides the single, trusted foundation that keeps business systems aligned from CRM to analytics. By defining core entities, such as customers, products, and suppliers, once, organizations reduce errors, improve reporting, and enable automation. Whether through structured MDM programs or simple shared datasets, mastering your data ensures consistent insights, stronger compliance, and readiness for AI-driven decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions
These quick answers cover the essentials, including what master data encompasses, how it differs from other data types, and who is responsible for managing it within an organization.
-
What is a master data example?
-
A customer record with name, contact details, and a unique ID used across CRM, billing, and support systems.
-
Is MDM part of data governance?
-
Yes, master data management is a key component of data governance that ensures consistency, quality, and control across systems.
-
What are master data domains?
-
Domains are core business entities, including customers, products, suppliers, employees, and locations.
-
How is master data different from reference data?
-
Master data describes business entities; reference data defines allowed values or classifications (like country codes or currencies).
-
Can master data be real-time?
-
Yes, modern MDM systems can synchronize master data in real-time to keep records consistent across platforms.
-
Who owns master data?
-
Ownership typically sits with business data stewards or data governance teams, supported by IT for integration and quality control.
Last updated on




