Master Data Management (MDM) ensures that key information, such as customer, product, and supplier data, remains reliable and synchronized across systems. This guide explains what MDM is, how it works, and why it’s vital for organizations aiming to stay insight-led in 2026 and beyond.
Key Takeaways:
- MDM ensures accurate, consistent data across all business systems.
- Unified data improves decisions, efficiency, and compliance.
- Parseur helps automate the extraction of clean data to power your MDM strategy.
In every modern business, data runs the show. From customer records and supplier details to product catalogs and financial systems, every process relies on having accurate and consistent information. But as organizations grow, so do their data silos, and small inconsistencies can quickly lead to duplicated records, reporting errors, and costly decisions.
According to Gartner, poor data quality costs organizations an average of $12.9 million per year, a figure that underscores the importance of maintaining clean, unified information across systems. That’s where Master Data Management (MDM) comes in.
That’s where Master Data Management (MDM) comes in. Master data refers to the core, trusted information about your key business entities, the single source of truth for customers, products, suppliers, and employees. MDM is the discipline and technology framework that keeps this data clean, connected, and consistent across all systems and teams.
In this complete 6 guide, we’ll explain what MDM is, how it works, and why it’s essential for organizations that are based on insights. You’ll learn how businesses use MDM to eliminate data chaos, improve decision-making, and build a unified foundation for analytics, AI, and automation.
What Is Master Data?
Master data is the essential, non-transactional information that defines your core business entities, the things your organization relies on daily. These include customers, suppliers, products, employees, locations, and accounts. In other words, it’s the shared reference point that different systems use to stay aligned.

Think of master data as the who and what behind your business. It describes the entities that appear repeatedly across multiple systems, such as your CRM, ERP, HR platform, and analytics tools, ensuring they all refer to the same information.
It’s important to distinguish master data from other types of data:
- Transactional data captures business events, such as sales orders, payments, or shipments.
- Reference data defines allowable values or categories, such as currency codes, country lists, or product types.
To make this concrete:
- When a retailer processes an online order, the customer and product are part of master data, while the order itself is transactional data.
- A logistics company relies on master data for warehouse locations and carriers, while the shipments they process are transactions.
- In HR, employee profiles (master data) feed into payroll or attendance systems that handle daily transactions.
What Is Master Data Management (MDM)?
Master Data Management (MDM) is the practice of creating a single, trusted view of key business data shared across systems and departments. It combines organizational processes, governance standards, and technology to ensure that master data remains accurate, consistent, and up-to-date everywhere it’s used.
At its core, MDM aims to eliminate duplication and confusion by maintaining a “golden record,” the unified, verified version of each business entity, whether that’s a customer, supplier, product, or employee. This golden record acts as the single source of truth, ensuring that every system, report, and decision is based on the same reliable information.
According to Dataversity, 92 % of businesses admit they have duplicate records in their systems, and over 70 % believe that a single view of the customer would lead directly to cost savings.
It’s helpful to think of MDM in two dimensions:
- MDM as a process: Establishes governance by defining who owns the data, how it’s maintained, and the rules for ensuring quality.
- MDM as a technology: Provides the tools and platforms that clean, match, merge, and distribute master data across systems in real time.
These elements form the foundation of trustworthy business intelligence and smooth operational workflows. Without MDM, inconsistent, outdated, or incomplete data can undermine even the most advanced analytics or AI models.
Why Is Master Data Management Important?
In a world where every business decision relies on data, Master Data Management (MDM) ensures that information is accurate, consistent, and readily usable. Without it, organizations face fragmented systems, duplicate records, and conflicting reports, all of which slow down decision-making and erode trust in data.
A recent survey by Melissa found that 84% of enterprises struggle with inaccurate or duplicate data, creating operational inefficiencies and confusion across departments. When multiple systems hold slightly different versions of the same customer or product record, routine tasks like reporting or forecasting can become unreliable.
The impact extends beyond inconvenience. According to Gitnux, 61% of organizations say data inconsistency issues directly affect their decision-making, often leading to missed opportunities or misguided strategies. By establishing a single, unified source of truth through MDM, businesses can eliminate these discrepancies and make decisions based on facts rather than assumptions.
Here are the key reasons MDM has become essential for modern enterprises:
Data Accuracy and Consistency
MDM ensures that every department works from the same verified information. When a customer’s name or product code appears differently across systems, MDM resolves those discrepancies and maintains a unified record.
Better Decision-Making and Reporting
Accurate master data underpins reliable analytics and business intelligence. With a consistent foundation, organizations can generate meaningful insights, forecast trends, and make faster, more informed decisions.
Improved Customer Experience
When customer data is unified, interactions feel seamless from marketing campaigns to support tickets. MDM helps companies recognize customers across channels, personalize engagement, and reduce friction caused by incomplete or outdated records.
Regulatory Compliance
Data privacy laws, such as GDPR and CCPA, require companies to know where personal data resides and how it’s used. MDM supports compliance by creating traceable, governed data structures with clear ownership and auditability.
Cost Savings and Operational Efficiency
Poor data quality costs organizations at least US$12.9 million annually on average, according to Gartner. By eliminating duplicate records and manual reconciliation, MDM reduces wasted effort and simplifies data-informed operations.
How Does Master Data Management Work?
Master Data Management (MDM) brings structure and consistency to business data by following a defined workflow. It connects multiple systems, cleans and confirms the information they contain, and distributes a single, trusted version back to the organization.
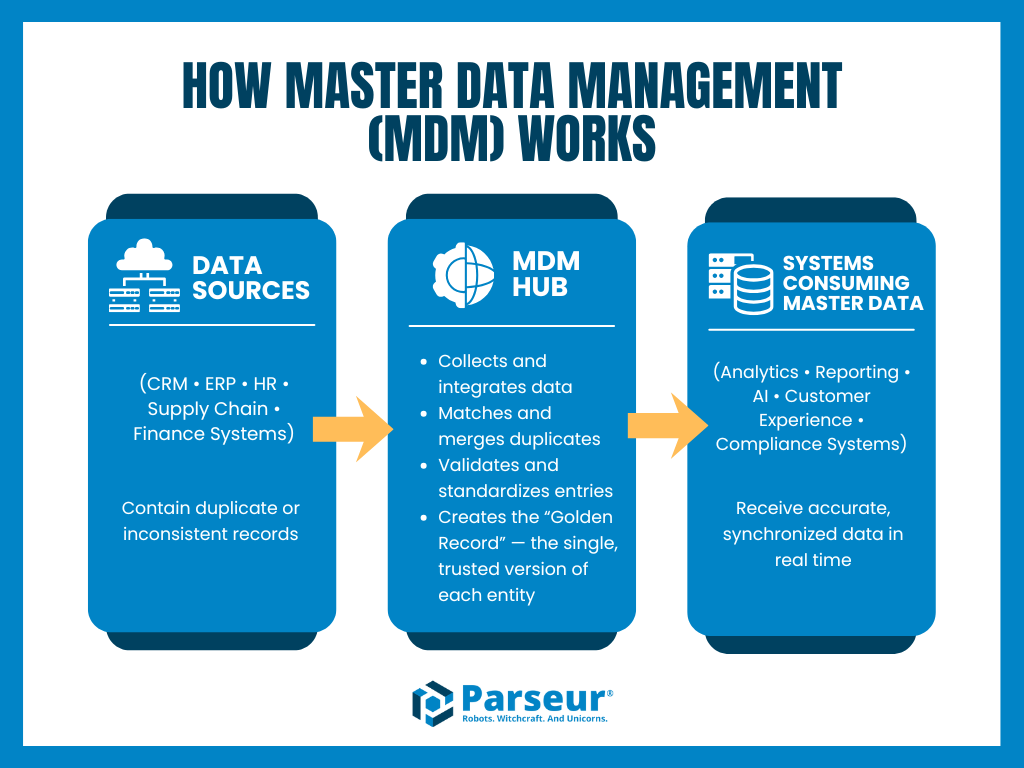
Here’s how the process typically works:
- Data Collection from Multiple Systems: MDM collects master data from various sources, including CRM, ERP, HR, and supply chain platforms. Each system may store slightly different versions of the same entity. For example, a customer name is spelled differently, or a product is listed under multiple SKUs.
- Data Matching and Deduplication: Advanced algorithms identify and merge duplicate or conflicting records. Matching ensures that “Jane Doe” in the CRM and “J. Doe” in the billing system are recognized as the same individual.
- Validation and Standardization: Once records are merged, MDM verifies fields (like email formats, addresses, or product codes) and enforces standard naming conventions. This step ensures that every record adheres to consistent rules and formats across all systems.
- Golden Record Creation: The system creates a “golden record” that combines the most accurate and up-to-date information from all sources to form a single, authoritative version of each entity. This golden record becomes the master reference point for the organization.
- Data Distribution and Synchronization: Finally, the golden record is distributed back to the connected systems. Updates to master data are automatically synchronized, ensuring that every department operates with the same information in real-time.
Hub-and-Spoke Architecture
Most MDM set-ups follow a hub-and-spoke model, where the MDM platform acts as the central hub. The hub receives, processes, and maintains master data, while connected business systems (the “spokes”) consume and update that data as needed. This model simplifies control, ensures consistency, and reduces data drift between systems.
Key Components Of Master Data Management (MDM)
Effective Master Data Management (MDM) brings together several core components that work in harmony to maintain reliable, governed, and secure master data across the organization. Each plays a distinct role in ensuring data quality and trustworthiness.
1. Data Governance
Data governance establishes the policies, roles, and responsibilities that guide the creation, maintenance, and use of master data. It defines ownership and accountability through data stewardship, ensuring consistency and compliance with business rules.
2. Data Quality Management
This component focuses on cleaning, standardizing, and enriching master data to remove duplicates, fix inconsistencies, and fill in missing details. The goal is to maintain accurate and complete data that meets business and regulatory standards.
3. Metadata Management
Metadata management documents the meaning, relationships, and lineage of data across systems. It helps users and systems understand what each field represents, promoting transparency and consistent interpretation of master data.
4. Integration
Integration ensures that master data flows smoothly between CRMs, ERPs, HR platforms, and analytics tools. By synchronizing updates in real time or through APIs, organizations maintain a unified view across all business applications.
5. Security and Compliance
Security and compliance protect master data through access controls, encryption, and audit trails, ensuring its integrity and confidentiality. These measures safeguard sensitive information and ensure compliance with data protection regulations, including GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
Common Challenges in Master Data Management
Adopting Master Data Management (MDM) can deliver enormous value, but success depends on addressing a few common challenges that organizations often face. Recognizing these early and planning accordingly helps ensure smoother adoption and lasting results.
1. Data Silos and Inconsistent Sources
When departments maintain separate systems, data becomes fragmented and inconsistent. This approach involves breaking down silos through integration and establishing shared governance policies, ensuring that every system refers to the same master record.
2. Lack of Executive Support or Governance
MDM initiatives often fail without clear leadership and accountability. Executive sponsorship and defined data ownership roles (like data stewards) ensure that master data remains a strategic business asset, not just an IT project.
3. Poor Data Quality or Missing Standards
Duplicate, incomplete, or inaccurate records can undermine the entire MDM effort. Setting up standardized data entry rules, implementing automated validation, and conducting periodic audits helps maintain clean and trusted master data.
4. Integration Complexity with Legacy Systems
Older systems may lack modern APIs or consistent data structures, making synchronization difficult. Middleware tools, data virtualization, and phased integration strategies can help bridge the gap without disrupting core operations.
5. Change Management and User Adoption
Even the best MDM tools fail if users don’t understand or trust them. Clear communication, training, and showing tangible business value, such as faster reporting or fewer errors, which drive adoption across teams.
Benefits and ROI of Master Data Management (MDM)
When adopted effectively, Master Data Management (MDM) delivers measurable results that go far beyond cleaner spreadsheets. By ensuring that all systems share accurate and consistent information, MDM strengthens every aspect of operations, from reporting and compliance to customer experience and analytics.
According to Semarchy, businesses that launch MDM approaches have seen up to a 20% improvement in data quality, and many report an average 10% reduction in operational costs thanks to fewer manual data correction tasks.
1. Reduced Operational Errors
With a single, trusted source of truth, teams spend less time reconciling conflicting data and correcting mistakes. Automated data synchronization reduces manual entry errors and eliminates duplicate records across departments.
2. Faster and More Reliable Reporting
Consistent master data enables finance, marketing, and operations teams to generate reports from the same baseline, reducing reconciliation time and enhancing confidence in insights. Many organizations state that reporting cycle times have been reduced by days or weeks.
3. Stronger Compliance and Audit Trails
MDM centralizes control over sensitive information, making it easier to track the origin of data and its changes. This enhances auditability and simplifies compliance with privacy regulations, such as GDPR or SOX.
4. Improved Analytics and AI Readiness
Clean, standardized data is the foundation for advanced analytics and machine learning. With MDM in place, organizations can trust their datasets, enabling better predictions, smarter automation, and faster innovation.
| Area | Without MDM | With MDM |
|---|---|---|
| Data consistency | Frequent duplicates and mismatched records | Unified, verified master data |
| Reporting | Delays and conflicting numbers | Faster, trusted reports |
| Compliance | Hard-to-trace data lineage | Clear audit trails |
| Operational efficiency | Manual corrections and rework | Automated, error-free workflows |
| Analytics & AI | Unreliable training data | Accurate, ready-to-use datasets |
Types of MDM Architectures
Different organizations structure Master Data Management (MDM) systems in various ways depending on their size, complexity, and integration needs. The main types of MDM architectures differ in where master data is stored and how it’s synchronized across systems.
1. Centralized MDM
In a centralized model, all master data is stored and maintained in a single hub. This system becomes the authoritative source, and all applications read and update data through it. It offers the highest level of consistency but can require significant integration changes to existing systems.
2. Registry MDM
The registry approach leaves master data in its original systems but maintains a central index or registry that links records. Instead of storing complete copies, it references where each piece of data lives, providing visibility without disrupting source systems.
3. Coexistence MDM
In the coexistence model, the central MDM hub and source systems continuously share updates. Changes made in one system are synchronized across others, maintaining consistency while allowing departments to keep control of their own data.
4. Consolidation MDM
The consolidation architecture pulls copies of master data from multiple systems into a central repository for cleansing and reporting. Source systems still operate independently, but the hub provides a unified, analytics-ready view of the data.
Most modern MDM platforms use hybrid or cloud-based architectures that blend these models. Cloud MDM solutions simplify scaling, integrating APIs, and synchronizing data in real-time across distributed environments, even without the heavy infrastructure demands of traditional systems.
MDM Tools and Software (Overview)
Master Data Management (MDM) tools provide the technology backbone that enables organizations to create, maintain, and distribute accurate master data across systems. These platforms combine data quality, integration, and governance capabilities to ensure that every team and application uses the same trusted information.
In practical terms, MDM software handles core functions such as:
- Data matching and merging: Identifying and consolidating duplicate records across systems.
- Data stewardship: Allowing human oversight for reviewing and approving changes to master data.
- Integration and synchronization: Connecting data between CRMs, ERPs, HR, and other business systems through APIs or middleware.
- Workflow automation: Streamlining approvals, updates, and alerts to maintain ongoing data accuracy and compliance.
The MDM market includes several categories of tools:
- Enterprise-grade platforms offered by large vendors, such as Informatica, SAP, IBM, and Microsoft, are designed for complex, global organizations that manage multiple data domains.
- Mid-market solutions are designed for businesses that require flexible MDM capabilities without the complexity or high costs associated with enterprise-level solutions.
- Open-source and community-driven tools which is suitable for smaller teams or organizations seeking flexibility and customization through self-managed setups.
Most modern MDM tools now support cloud-based or hybrid architectures, offering easier integration, real-time updates, and AI-powered data matching. As the market evolves, businesses can expect increased automation, reduced setup overhead, and more comprehensive analytics integration.
Implementing an MDM Strategy
Building an effective Master Data Management (MDM) strategy requires a structured, step-by-step approach that matches technology, people, and business goals. The objective is to establish a sustainable framework for maintaining accurate, consistent, and trustworthy data throughout the organization.
1. Define Business Goals and Data Domains
Start by identifying what your organization wants to achieve with MDM, for example, improving reporting accuracy, reducing customer duplication, or enhancing regulatory compliance. Then, determine which data domains (such as customers, products, suppliers, etc.) are most critical to achieving those goals.
2. Get Stakeholder and Executive Buy-In
Successful MDM requires alignment across departments. Secure executive sponsorship and involve business leaders early to ensure the initiative has visibility, budget, and long-term support.
3. Establish Data Governance and Policies
Define how data will be created, maintained, and shared. Assign data stewards, set validation rules, and apply ownership and access control policies. Governance ensures consistency and accountability throughout the data lifecycle.
4. Choose Technology and Architecture
Select an MDM platform and architecture model, whether centralized, coexistence, or hybrid, that fits your organization’s size, infrastructure, and integration needs. Look for scalability, security, and flexibility for future growth.
5. Clean and Migrate Existing Data
Before populating the MDM hub, audit and clean existing data to remove duplicates, fix inconsistencies, and standardize formats. This ensures that only accurate, verified information enters the system from day one.
6. Train Teams and Measure Success
Provide hands-on training for both technical and business users. Define KPIs such as data accuracy rates, duplicate reduction, or report turnaround times to measure the success of your MDM rollout.
Start Small, Then Expand
Begin with one high-impact data domain, such as customer or product data, and refine your processes before scaling to other areas. This phased approach reduces risk, demonstrates value early, and helps teams adapt smoothly to new workflows.
MDM and Other Data Disciplines
Master Data Management (MDM) doesn’t exist in isolation. It works in conjunction with other key data disciplines to ensure that information across the enterprise is accurate, governed, and ready for analytics and AI. Here’s how MDM connects with related fields:
MDM vs. Data Governance
Data Governance defines the policies, roles, and standards that determine how data is managed and used. MDM operationalizes those rules by enforcing data quality, ownership, and consistency in practice. Governance sets the “rules of the road,” while MDM ensures every system follows them.
MDM vs. Data Integration
Data Integration focuses on moving and synchronizing data between systems. MDM ensures that the integrated data is clean, standardized, and uniquely identified. Integration connects systems; MDM ensures what flows between them is correct.
MDM vs. Data Warehouse
A Data Warehouse stores historical and transactional data for analytics and reporting. MDM feeds the warehouse with accurate, consistent master records, serving as the single source of truth for entities such as customers or products. In essence, MDM governs the “who” and “what,” while the warehouse handles the “how much” and “when.”
MDM and AI / Machine Learning
Accurate master data is the foundation of effective AI and ML models. Without trusted entity data, algorithms may misclassify, duplicate, or misinterpret inputs. MDM provides the clean, unified datasets that power reliable predictions and advanced analytics.
Future of Master Data Management
As data ecosystems become increasingly distributed and dynamic, Master Data Management (MDM) continues to evolve to meet new business and technical requirements. The future of MDM centers on flexibility, intelligence, and real-time connectivity, ensuring that organizations can trust and act on their data, regardless of where it resides.
Cloud-Native MDM
Modern MDM approaches are increasingly built for the cloud, offering scalability, lower infrastructure costs, and easier integration with SaaS systems. Cloud-native MDM enables real-time updates and global collaboration, supporting hybrid and multi-cloud environments that reflect how organizations operate today.
AI-Driven Data Matching and Anomaly Detection
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are transforming traditional data matching, enabling systems to identify duplicates, inconsistencies, and anomalies with higher precision. These capabilities help maintain cleaner master data without constant manual intervention, improving both accuracy and efficiency.
MDM as Part of Data Fabric or Data Mesh
As organizations move away from centralized data architectures, MDM is being reimagined as a component of broader data fabric and data mesh strategies. In this model, MDM provides shared data standards and governance across decentralized domains, maintaining consistency while allowing local ownership.
Real-Time Synchronization Across Applications
The change toward event-driven architectures means MDM must support continuous synchronization between applications. Instead of periodic batch updates, future MDM platforms will ensure that changes, such as a customer address update or a product price change, are reflected instantly across all systems.
Why Master Data Management Is the Foundation Of Data-Driven Success
Master Data Management (MDM) provides the foundation for reliable, unified data across all systems and departments. By creating a single source of truth for key entities, such as customers, products, and suppliers, MDM enhances decision-making, improves compliance, and facilitates seamless collaboration. As organizations adopt automation, analytics, and AI, trusted master data becomes increasingly critical to their success.
Reliable data powers automation and AI. Tools like Parseur help extract and prepare clean, structured data that can be fed directly into your MDM strategy, setting the stage for smarter, more connected operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Before diving deeper or starting your own MDM initiative, it’s natural to have a few key questions. Below, we’ve compiled concise answers to the most common queries about Master Data Management (MDM), what it is, how it works, and why it’s essential for maintaining reliable, unified data across modern enterprises.
-
What is a master data example?
-
Master data refers to core business entities shared across systems, such as customers, suppliers, products, or employees. For example, a customer profile containing name, contact details, and account ID is a piece of master data used across multiple applications.
-
Is MDM part of data governance?
-
Yes. MDM is a key operational component of data governance, enforcing the policies, standards, and ownership rules defined by governance frameworks to ensure consistent and accurate data across the organization.
-
What are master data domains?
-
Master data domains group similar types of core entities, such as Customer, Product, Supplier, Employee, and Location. Each domain has its own rules, relationships, and attributes that define how data is stored and shared across systems.
-
What is the difference between master and transactional data?
-
Master data describes who or what is involved in a business process (e.g., customers, products). Transactional data records events or activities—such as sales, orders, or payments, where master data entities interact.
-
How does MDM support AI and analytics?
-
AI and analytics rely on clean, unified data. MDM ensures that all information feeding machine learning models and analytics tools is accurate, consistent, and complete, leading to better predictions, insights, and automation outcomes.
-
Who is responsible for managing master data?
-
Typically, data stewards, business analysts, and IT teams share responsibility. Data stewards maintain quality and standards, while IT teams manage integration and system synchronization.
-
How long does it take to complete MDM?
-
Completion time varies by scope. Small projects focused on a single data domain may take 3–6 months, while enterprise-wide MDM initiatives can extend to 12–18 months, depending on the system's complexity and governance maturity.
Last updated on




